Openc学习札记:关于反投影直方图
Openc学习笔记:关于反投影直方图直方图是图像内容的一个重要特性。如果一副图像的区域中显示的是一种独特的
Openc学习笔记:关于反投影直方图
直方图是图像内容的一个重要特性。如果一副图像的区域中显示的是一种独特的纹理或是一个独特的物体,那么这个区域的直方图可以看作是一个概念函数,它给出的是某个像素属于该纹理或物体的概率。基于上述想法,我们可以利用反向投影直方图来检测特定的图像内容。
而所谓的反向投影就是一种记录给定图像中的像素点如何适应直方图模型像素分布的方式。简单的讲, 所谓反向投影就是首先计算某一特征的直方图模型,然后使用模型去寻找图像中存在的该特征。说到这里,可能大家还是有点儿糊涂,其实具体来说,图像的反向投影图是用输入图像的某一位置上像素值(多维或灰度)对应在直方图的一个bin上的值来代替该像素值(bin上的值越大就代表着这个像素值出现的概率越大),所以得到的反向投影图是单通的。用统计学术语,输出图像象素点的值是观测数组在某个分布(直方图)下的概率。
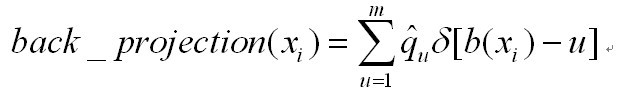
其中b(xi)表示在位置xi上像素对应的直方图第b(xi)个bin,直方图共m个bin,qu表示第u个bin的值。在OpenCV里面,有一个专门的函数calcBackProject来进行反投影直方图计算。
Calculates the back projection of a histogram.
参数:
- arrays – Source arrays. They all should have the same depth,
- Before the tracking, show the object to the camera such that covers almost the whole frame. Calculate a hue histogram. The histogram will likely have a strong maximums, corresponding to the dominant colors in the object.
- During the tracking, calculate back projection of a hue plane of each input video frame using that pre-computed histogram. Threshold the back projection to suppress weak colors. It may also have sense to suppress pixels with non sufficient color saturation and too dark or too bright pixels.
- Find connected components in the resulting picture and choose, for example, the largest component.
That is the approximate algorithm of CAMShift() color object tracker.
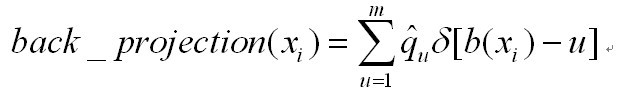 其中b(xi)表示在位置xi上像素对应的直方图第b(xi)个bin,直方图共m个bin,qu表示第u个bin的值。在OpenCV里面,有一个专门的函数calcBackProject来进行反投影直方图计算。
其中b(xi)表示在位置xi上像素对应的直方图第b(xi)个bin,直方图共m个bin,qu表示第u个bin的值。在OpenCV里面,有一个专门的函数calcBackProject来进行反投影直方图计算。