Java紼嬪簭璋冧紭---鍘繪帀 java 欏圭洰涓?澶氫綑鐨刯ar鍖?鏂規硶
Eclipse by default starts its VM with a very small heap and stack. This leads to some mysterous stack overflows from within Eclipse when plugins are performing long running jobs. This is a well documented bug within Eclipse that affects other plugins. The work around is to increase the stack size upon eclipse startup.
eclipse.exe -Xms64m
The Classpath Helper Views can be opened in any perspective with the following steps.
First, from the Menu select聽Window->Show View->Other...

Second, under the聽Classpath Helper聽category, select the聽Classpath Helper View,聽Location By Location View, or聽Packages View

The basic layout of this view should be a straight forward translation of the classpath. The classpath is based upon the currently selected聽model聽(which initially is taken from the currently selected Java Project from you聽Package Explorer聽view).
Familar icons are used for Jar files and class folders. The order is represented top to bottom. The various decorations on these elements will be explained later.
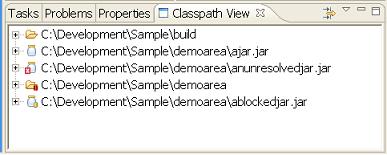
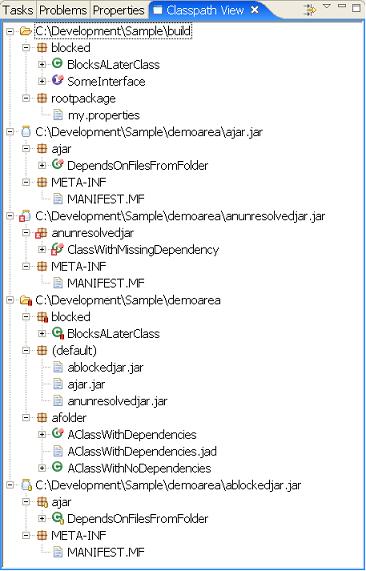
This can be expanded to show the classes and interfaces within each jar or folder.
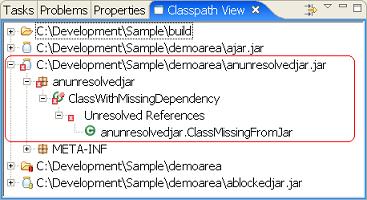
The highlighted region shows a jar and class file decorated with a聽 . This indicates that a reference to a class cannot be resolved (found) on the current classpath. In this example, a class called聽
. This indicates that a reference to a class cannot be resolved (found) on the current classpath. In this example, a class called聽anunresolvedjar.ClassMissingFromJar聽cannot be found. At runtime this would lead to either a聽java.lang.ClassNotFoundException聽or a聽java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. In either case, the class聽anunresolvedjar.ClassWithMissingDependency聽cannot be loaded.

The first highlighted region (next to the聽 ) shows jar and class file decorated with a聽
) shows jar and class file decorated with a聽 . This indicates a class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This means that the class/interface located at this location will never be loaded. Instead it is loaded from another location. In this instance, we can see that the class聽
. This indicates a class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This means that the class/interface located at this location will never be loaded. Instead it is loaded from another location. In this instance, we can see that the class聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolder聽will actually be loaded from聽C:\Development\Sample\demoarea\ajar.jar.
In the second highlighted region (next to the聽 ) we can see the class聽
) we can see the class聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolder. Although not a critical problem with the classpath, it could be confusing if the jar聽C:\Development\Sample\demoarea\ablockedjar.jar聽is updated with a new instance of聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolder聽as the newer class will never get loaded into the JVM.

The first highlighted region (next to the聽 聽shows a folder and class file with a聽
聽shows a folder and class file with a聽 . This indicates a class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This is essentially the same as a yellow rectangle with one addition. The red color is also an indication that the version of the class at this location (
. This indicates a class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This is essentially the same as a yellow rectangle with one addition. The red color is also an indication that the version of the class at this location (C:\Development\Sample\demoarea聽in this example) is different from the version that will actually be loaded (from聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽in this example). As with a yellow rectangle, the folder shown below the聽blocked聽class is the location where the class will actually get loaded from.
As with the previous example, the second highlight聽 聽is showing the folder where the actual class will get loaded from. Of course blocking locations will always be above (appear earlier) in the classpath.
聽is showing the folder where the actual class will get loaded from. Of course blocking locations will always be above (appear earlier) in the classpath.

Classes decorated with the聽 聽image indicates a class that is not referenced by any other class. In the above image聽
聽image indicates a class that is not referenced by any other class. In the above image聽afolder.AClassWithDependencies聽is not referenced by any other class. Keep in mind that this information is based solely on references maintained within the classfile itself.聽There are several notable cases where class files are referenced but this will not be indicated including:
Class.forName()聽is used to load a classes, which is common in many frameworks including struts, WAR web.xml files, EJB descriptors, etc.static final聽constants) are compiled inline. This means that although there's a compile time dependency on the constants at runtime there is no reference to the declaring interface/class.聽
Class聽or聽Interface聽Depends On
In addition to showing issues or problems with the classpath, Classpath Helper also can be used to show what classes/interfaces a particular class depends on. The highlighted region shows that the class聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolder聽depends on
afolder.AClassWithNoDependencies聽loaded from聽C:\Development\Sample\demoareablocked.BlocksALaterClass聽loaded from聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽

In addition to showing locations and classes a class depends on, it is also possible to see which classes refer to a given class. In the above image you can see the class聽SomeInterface聽is referenced by聽blocked.BlocksALaterClass聽(which is located in the聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽folder).
 聽
聽
 聽
聽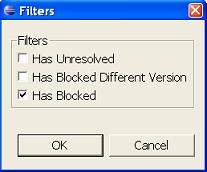
 聽
聽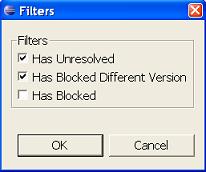
 聽
聽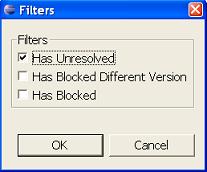
It is possible to apply filtering to the Classpath Helper view. Filtering will only show jars/folders/classes/packages that relate to selected filtering criteria.
The layout of this view initially appears identical to the ClasspathHelper view, however it is intended to show relationships between jars. The decorative icons are the same and essentially have the same meaning. But the Location by Location view can be used to view inter jar information.
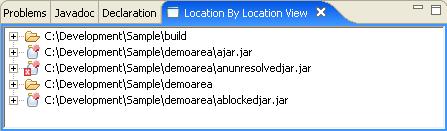
This can be expanded in a similar fashion.
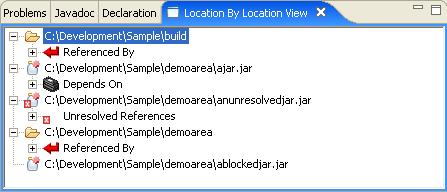
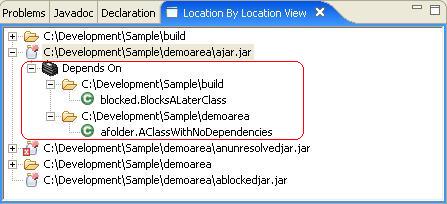
The Depends on branch shows which jars/folders that this particular jar depends on. In this case聽ajar.jar聽depends on both the聽build聽and聽demoarea聽folders. Within each folder we can see the specific classes that are depended on.
Also notice the unreferenced icon聽 . As with the classpath helper view, this indicates that the object is unreferenced. However in this view the icon indicates a jar that is not referenced at runtime by any other jar. This can be useful in locating obsolete jars.
. As with the classpath helper view, this indicates that the object is unreferenced. However in this view the icon indicates a jar that is not referenced at runtime by any other jar. This can be useful in locating obsolete jars.
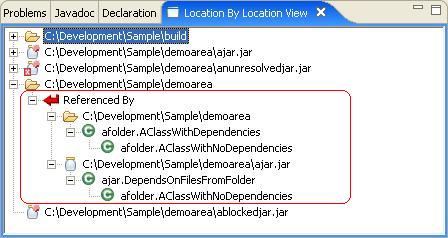
The Referenced by Branch is the reverse of the depends on view. It shows which jars a particular jar supports or is referred to by. In this case,聽demoarea聽is referenced by itself and聽ajar.jar. The references are聽afolder.AClassWithDependencies聽and聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolders. The specific class referenced isafolder.AClassWithNoDependencies聽which is refered to by both.
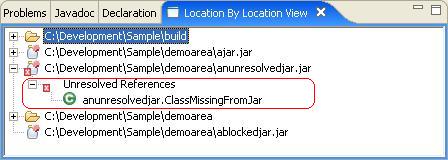
The unresolved branch is similar to unresolved branch from the ClassPath view. The only difference is that it is showing a summary of unresolved classes for the entire jar. In this case聽anunresolvedjar.ClassMissingFromJar聽cannot be found.
This view takes a package centric view of the classpath, allowing you to look for classes without knowing or caring about the location of the class. The decorative icons are the same and have the same meaning as the other views.
Packages can be expanded to reveal the contents of a package.
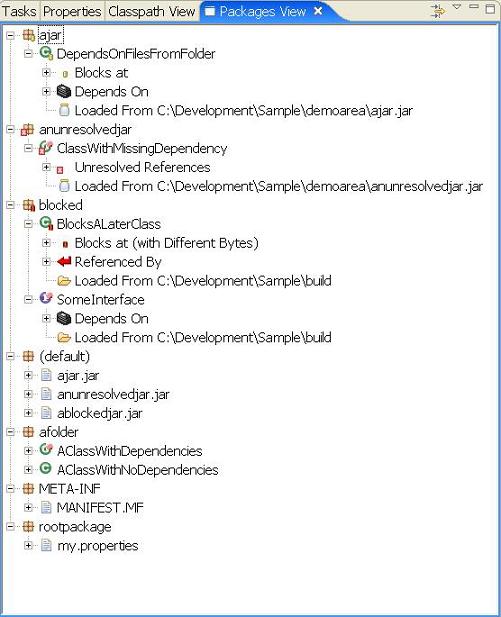
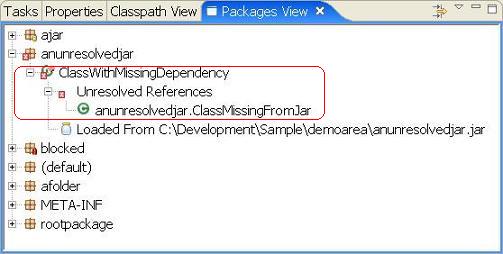
The highlighted region shows a package and class file decorated with a聽 . This indicates that a reference to a class cannot be resolved (found) on the current classpath. In this example, a class called聽
. This indicates that a reference to a class cannot be resolved (found) on the current classpath. In this example, a class called聽anunresolvedjar.ClassMissingFromJar聽cannot be found. At runtime this would lead to either a聽java.lang.ClassNotFoundException聽or a聽java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. In either case, the class聽anunresolvedjar.ClassWithMissingDependency聽cannot be loaded.
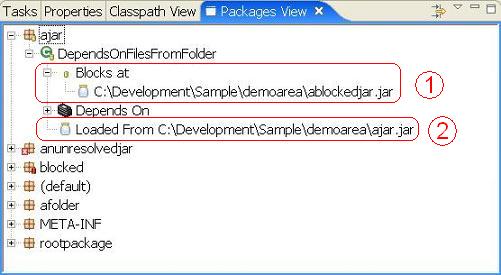
The first highlighted region (next to the聽 ) shows the class file聽
) shows the class file聽DependsOnFilesFromFolder聽decorated with a聽 . This indicates the class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This means that the class/interface is available at multiple locations on the classpath. The list shows areas where this class is blocked.
. This indicates the class is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This means that the class/interface is available at multiple locations on the classpath. The list shows areas where this class is blocked.
The second highlighted region (next to the聽 ) shows where the class would actually be loaded from.
) shows where the class would actually be loaded from.
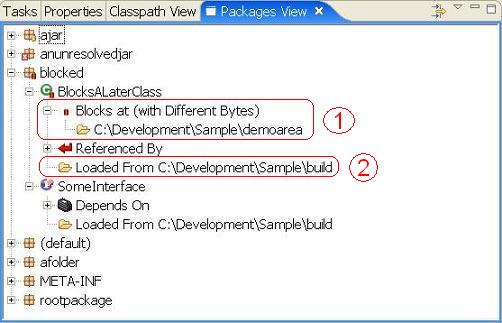
The first highlighted region (next to the聽 聽shows the class聽
聽shows the class聽BlocksALaterClass聽file with a聽 . This indicates it is is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This is essentially the same as a yellow rectangle with one addition. The red color is also an indication that the version of the class at this location (
. This indicates it is is 'blocked' or 'obscured' on the classpath. This is essentially the same as a yellow rectangle with one addition. The red color is also an indication that the version of the class at this location (C:\Development\Sample\demoarea聽in this example) is different from the version that will actually be loaded (from聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽in this example). As with a yellow rectangle, the folder shown below the聽blocked聽class is the location where the class will actually get loaded from.
As with the previous example, the second highlight聽 聽is showing the folder where the actual class will get loaded from. Of course blocking locations will always be above (appear earlier) in the classpath.
聽is showing the folder where the actual class will get loaded from. Of course blocking locations will always be above (appear earlier) in the classpath.
Class聽or聽Interface聽Depends On
In addition to showing issues or problems with the classpath, Classpath Helper also can be used to show what classes/interfaces a particular class depends on. The highlighted region shows that the class聽ajar.DependsOnFilesFromFolder聽depends on
afolder.AClassWithNoDependencies聽loaded from聽C:\Development\Sample\demoareablocked.BlocksALaterClass聽loaded from聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽

In addition to showing locations and classes a class depends on, it is also possible to see which classes refer to a given class. In the above image you can see the class聽SomeInterface聽is referenced by聽blocked.BlocksALaterClass聽(which is located in the聽C:\Development\Sample\build聽folder).
 聽
聽
 聽
聽
 聽
聽
 聽
聽
It is possible to apply filtering to the Classpath Helper view. Filtering will only show jars/folders/classes/packages that relate to selected filtering criteria.
This view scans for jars that are not on the classpath (but are under the current project). It provides basic browsing of packages and classes that are available but not on the classpath. This can be helpful when trying to build up a classpath, as you can quickly browse for the missing classes to see which jars contain them.
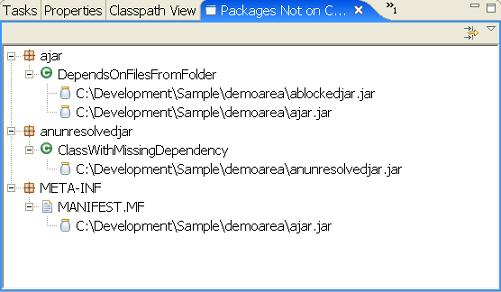
The only information this view shows is which jars a class or interface can be loaded from. Only jars from the current Eclipse project that are not already on the classpath are scanned (this image was created by removing previously demoed jars from the classpath).
鎻掍歡浜岋細Classpath Checker
鎻掍歡鍦闆潃錛歨ttp://classpathchecker.free.fr/
Classpath Checker @ Eclipse Plugin Central
As you know, current java projects depend of more and more external libraries, and 3rd party products. Obviously, each 3rd party product embeds its own libraries, consequently it becomes very difficult to be sure there are no classpath problems in the application. One terrible behavior is when the libraries order becomes important in the classpath! That's why Classpath Checker can help you.
After installing the plugin, you have to right click on your java project, then select "Properties".
The following dialog is displayed, select the "Classpath Checker" section, and then check the "Activate classpath checker".