java网络编程笔记
1 TCP的开销
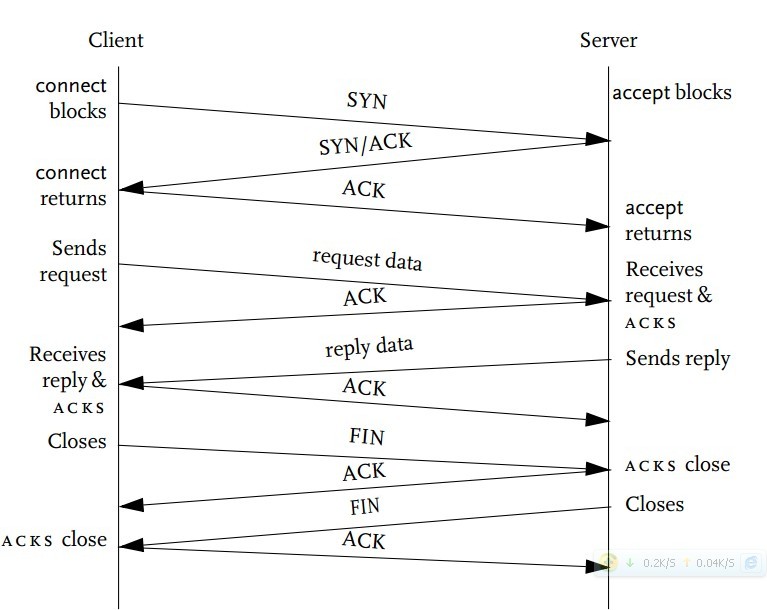
a ?连接协商三次握手,c->syn->s,s->syn ack->c, c->ack->s
b ?关闭协商四次握手,c->fin->s, s->ack-c,s->fin->c,c->ack->s
c ?保持数据有序,响应确认等计算开销
d ?网络拥塞引起的重试开销
2 使用知名端口初始化 serversocket可能需要超级权限。ServerSocket(int port, int backlog)参数backlog用来配置连接队列,在accept之前预先完成连接,加速连接TCP连接阶段,默认为50.
?
backlog表示ServerSocket可以接受的同时最大连接数量,超过这个连接数量,将会拒绝连接。
?
如果要提高吞吐量,可以通过设置更大的ServerSocket.setReceiveBufferSize来实现,但是必须在bind之前设置,也就是说要先调用无参构造,然后再调用ServerSocket.bind(SocketAddress endpoint)
?
3 网络io写操作,提高吞吐量较好的实践有使用java.io.BufferedOutputStream,作为缓冲,减少用户线程和内核线程的切换频率。缓冲区大小一般大于ServerSocket.setReceiveBufferSize。
?
4 避免对象流死锁,较好的实践是如果要在同一个socket上构建对象输入流和输出流,最好是先构造输出流,再构造输入流。
?
5 tcp半关闭,shut down output,完成后,对方的read收到eof,结束阻塞。
?
6 tcp关闭可以用socket.close,socket.getoutputstream.close,socket.getinputstream.close,较好的方式是调用socket.getoutpurtstream.close,它会把未flush的flush掉。三个方法只需调用其中一个即可。isClose方法只会告诉我们本地tcp是否关闭,但是不能告诉我们远程是否关闭。
?
7 socket read 设置timeout时间,防止无止境阻塞。一般来说,timeout时间会设定为预期时间的两倍。timeout时间设置只对之后的阻塞读有效。
?
8 每个socket都有send buffer和receive buffer,这个buffer在内核地址空间而非jvm。buffer的size由操作系统实现决定,一般来说是2kb。send buffer可以在tcp关闭前随时设定,通过java.net.Socket.setSendBufferSize(int)设置。但是size的设置只是一种hint,不是绝对值。size设得越大,减少网络写次数,减少拥塞控制,tcp效率、吞吐量越高,类似http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nagle's_algorithm?原理。
一般设定为MSS的三倍;至少大于对方receive buffer;receive buffer也要设定大一点,不拖send buffer后腿;
bufferedoutputstream,bytebuffer一般也要设定为匹配的值;
buffersize(bits)=bandwidth(bits/sec)* delay(sec),有点类似于线程数量的控制,不让cpu闲下来。这边的白话是不让buffer空下来,随时处于最大填充状态。
?
9 nagle算法,为了提高网络传输效率,减少网络拥塞,延迟小包发送,组装为大包一起发送。默认为开,可以通过setTcpnodelay为true来关闭。一般来说,不会关闭,除非是需要实时交互的场景。另外如果真需要关闭,可以采用巧妙的方式,使用bufferedoutputstream,把buffer size设为大于最大请求或响应包,socket send buffer和receive buffer也设为此值,用一次操作写出请求或响应,bufferedoutputstream.flush,充分利用网络。
?
10 setlinger,用于关闭socket时,进行磨蹭,拖延。
?
11 keep alive,是个鸡肋。用于检测连接是否处于连接状态,检测对方是否active。它比较有争议,不是tcp协议的标准内容。另外检测需要消耗网络,当检测对方无反应,socket会被置为reset状态,不可读写。一般不推荐使用。
可以考虑用应用层的心跳检测替代。
参考http://hi.baidu.com/tantea/blog/item/580b9d0218f981793812bb7b.html
?
12 ?settrafficclass,设置流量类别,只是hint作用,具体效果取决于实现。有这些类别? IPTOS_LOWCOST (0x02),IPTOS_RELIABILITY (0x04),IPTOS_THROUGHPUT (0x08),IPTOS_LOWDELAY (0x10)
?
13 接口中文翻译http://hi.baidu.com/%EC%C5%BF%E1%D0%A1%B7%E5/blog/item/5d8e0f58aee147471038c29d.html
* ReliableDatagramSocket.java.* Copyright ? Esmond Pitt, 1997, 2005. All rights reserved.* Permission to use is granted provided this copyright* and permission notice is preserved.*/import java.io.*;import java.net.*;import java.text.*;import java.util.*;// All times are expressed in seconds.// ReliabilityConstants interface, just defines constants.interface ReliabilityConstants{// Timeout minima/maximapublic static final int MIN_RETRANSMIT_TIMEOUT = 1;public static final int MAX_RETRANSMIT_TIMEOUT = 64;// Maximum retransmissions per datagram, suggest 3 or 4.public static final int MAX_RETRANSMISSIONS = 4;}The D;; class manages current and smoothed round-trip timersand the related timeouts:// RoundTripTimer class.class RoundTripTimer implements ReliabilityConstants{float roundTripTime = 0.0f;// most recent RTTfloat smoothedTripTime = 0.0f;// smoothed RTTfloat deviation = 0.75f; // smoothed mean deviationshort retransmissions = 0;// retransmit count: 0, 1, 2, …// current retransmit timeoutfloat currentTimeout =minmax(calculateRetransmitTimeout());/** @return the re-transmission timeout. */private int calculateRetransmitTimeout(){return (int)(smoothedTripTime+4.0*deviation);}/** @return the bounded retransmission timeout. */private float minmax(float rto){return Math.min(Math.max(rto, MIN_RETRANSMIT_TIMEOUT),MAX_RETRANSMIT_TIMEOUT);}/** Called before each new packet is transmitted. */void newPacket(){retransmissions = 0;}/** * @return the timeout for the packet. */float currentTimeout(){return currentTimeout;}/** * Called straight after a successful receive. * Calculates the round-trip time, then updates the * smoothed round-trip time and the variance (deviation). * @param ms time in ms since starting the transmission. */void stoppedAt(long ms){// Calculate the round-trip time for this packet.roundTripTime = ms/1000;// Update our estimators of round-trip time// and its mean deviation.double delta = roundTripTime ? smoothedTripTime;smoothedTripTime += delta/8.0;deviation += (Math.abs(delta)-deviation)/4.0;// Recalculate the current timeout.currentTimeout = minmax(calculateRetransmitTimeout());}/** * Called after a timeout has occurred. * @return true if it's time to give up, * false if we can retransmit. */boolean isTimeout(){currentTimeout *= 2; // next retransmit timeoutretransmissions++;return retransmissions > MAX_RETRANSMISSIONS;}} // RoundTripTimer classThe D" class exports a D method like the oneswe have already seen.// ReliableDatagramSocket classpublic class ReliableDatagramSocketextends DatagramSocketimplements ReliabilityConstants{RoundTripTimer roundTripTimer = new RoundTripTimer();private boolean reinit = false;private long sendSequenceNo = 0; // send sequence #private long recvSequenceNo = 0; // recv sequence #/* anonymous initialization for all constructors */{init();}/** * Construct a ReliableDatagramSocket * @param port Local port: reeive on any interface/address * @exception SocketException can't create the socket */public ReliableDatagramSocket(int port)throws SocketException{super(port);}/** * Construct a ReliableDatagramSocket * @param port Local port * @param localAddr local interface address to use * @exception SocketException can't create the socket */public ReliableDatagramSocket(int port, InetAddress localAddr) throws SocketException{super(port, localAddr);}/** * Construct a ReliableDatagramSocket, JDK >= 1.4. * @param localAddr local socket address to use * @exception SocketException can't create the socket */public ReliableDatagramSocket(SocketAddress localAddr)throws SocketException{super(localAddr);}/** * Overrides DatagramSocket.connect(): * Does the connect, then (re-)initializes * the statistics for the connection. * @param dest Destination address * @param port Destination port */public void connect(InetAddress dest, int port){super.connect(dest, port);init();}/** * Overrides JDK 1.4 DatagramSocket.connect(). * Does the connect, then (re-)initializes * the statistics for the connection. * @param dest Destination address */public void connect(SocketAddress dest){super.connect(dest);init();}/** Initialize */private void init(){this.roundTripTimer = new RoundTripTimer();}/** * Send and receive reliably, * retrying adaptively with exponential backoff * until the response is received or timeout occurs. * @param sendPacket outgoing request datagram * @param recvPacket incoming reply datagram * @exception IOException on any error * @exception InterruptedIOException on timeout */public synchronized void sendReceive(DatagramPacket sendPacket, DatagramPacket recvPacket)throws IOException, InterruptedIOException{// re-initialize after timeoutif (reinit){init();reinit = false;}roundTripTimer.newPacket();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();long sequenceNumber = getSendSequenceNo();// Loop until final timeout or some unexpected exceptionfor (;;){// keep using the same sequenceNumber while retryingsetSendSequenceNo(sequenceNumber);send(sendPacket);// may throwint timeout =(int)(roundTripTimer.currentTimeout()*1000.0+0.5);long soTimeoutStart = System.currentTimeMillis();try{for (;;){// Adjust socket timeout for time already elapsedint soTimeout = timeout?(int)(System.currentTimeMillis()?soTimeoutStart);setSoTimeout(soTimeout);receive(recvPacket);long recvSequenceNumber = getRecvSequenceNo();if (recvSequenceNumber == sequenceNumber){// Got the correct reply:// stop timer, calculate new RTT valueslong ms = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;roundTripTimer.stoppedAt(ms);return;}}}catch (InterruptedIOException exc){// timeout: retry?if (roundTripTimer.isTimeout()){reinit = true;// rethrow InterruptedIOException to callerthrow exc;}// else continue }// may throw other SocketException or IOException} // end re-transmit loop} // sendReceive()/** * @return the last received sequence number; * used by servers to obtain the reply sequenceNumber. */public long getRecvSequenceNo(){return recvSequenceNo;}/** @return the last sent sequence number */private long getSendSequenceNo(){return sendSequenceNo;}/** * Set the next send sequence number. * Used by servers to set the reply * sequenceNumber from the received packet: *. * socket.setSendSequenceNo(socket.getRecvSequenceNo()); * * @param sendSequenceNo Next sequence number to send. */public void setSendSequenceNo(long sendSequenceNo){this.sendSequenceNo = sendSequenceNo;}/** * override for DatagramSocket.receive: * handles the sequence number. * @param packet DatagramPacket * @exception IOException I/O error */public void receive(DatagramPacket packet)throws IOException{super.receive(packet);// read sequence number and remove it from the packetByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(packet.getData(), packet.getOffset(),packet.getLength());DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);recvSequenceNo = dis.readLong();byte[] buffer = new byte[dis.available()];dis.read(buffer);packet.setData(buffer,0,buffer.length);}/** * override for DatagramSocket.send: * handles the sequence number. * @param packet DatagramPacket * @exception IOException I/O error */public void send(DatagramPacket packet)throws IOException{ByteArrayOutputStreambaos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();DataOutputStreamdos = new DataOutputStream(baos);// Write the sequence number, then the user data.dos.writeLong(sendSequenceNo++);dos.write(packet.getData(), packet.getOffset(),packet.getLength());dos.flush();// Construct a new packet with this new data and send it.byte[]data = baos.toByteArray();packet = new DatagramPacket(data, baos.size(), packet.getAddress(),packet.getPort());super.send(packet);}} // end of ReliableDatagramSocket classpublic class ReliableEchoServer implements Runnable{ReliableDatagramSocketsocket;byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];DatagramPacket recvPacket =new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);ReliableEchoServer(int port) throws IOException{this.socket = new ReliableDatagramSocket(port);}public void run(){for (;;){try{// Restore the receive length to the maximumrecvPacket.setLength(buffer.length);socket.receive(recvPacket);// Reply must have same seqno as requestlong seqno = socket.getRecvSequenceNo();socket.setSendSequenceNo(seqno);// Echo the request back as the responsesocket.send(recvPacket);}catch (IOException exc){exc.printStackTrace();}} // for (;;)} // run()} // classUDP支持多播和广播(广播是一种特殊的多播,尽量不使用广播,广播产生更多没必要的网络流量),而TCP只支持单播。一般多播用于服务发现,如jini look up。多播与多次单播相比,好处是减少开销、减小网络流量、减少服务器负载,而且速度更快,并且接受者接收到消息的时间更接近,对于某些场景来说很重要。
多播的缺点是继承了udp,不可靠网络,依赖路由器,安全问题更加复杂。并且多播并不知道多播消息会被哪些接受者接收,也不知道接受者是否接收到,设计协议的时候需要考虑这点。
发送多播消息,发送端可以用MulticastSocket和DatagramSocket,而接收端只能用MulticastSocket。
?
?
多播使用场景
?
(a) Software distribution
(b) Time services
(c) Naming services like
(d) Stock-market tickers, race results, and the like
(e) Database replication
(f) Video and audio streaming: video conferencing, movie shows, etc
(g) Multi-player gaming
(h) Distributed resource allocation
(i) Service discovery.
?
public void processSession(Socket socket){receive(request);// process request and construct reply, not shown …send(reply);// close connectionsocket.close();// exception handling not shown}?void processSession(Socket socket){while (receive(request)) // i.e. while not end-of-stream{// process request and construct reply, not shown …send(reply);}// close connectionsocket.close();// exception handling not shown}?多次对话的连接释放方式,可以根据输入流的返回结果,或者遇到eof来关闭连接。归结点(a) On receipt of an end-of-stream when reading the connection.(b) If the request or the client is deemed invalid.(c) On detection of a read timeout or idle timeout on the connection.(d) After writing a reply// Initialization - common to both endsstatic final int HEADER_LENGTH = 16;static final int BODY_LENGTH = 480;static final int TRAILER_LENGTH = 16;ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(HEADER_LENGTH);ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(BODY_LENGTH);ByteBuffer trailer = ByteBuffer.allocate(TRAILER_LENGTH);ByteBuffer[]buffers = new ByteBuffer[]{ header, body, trailer };// sending end - populate the buffers, not shownlong count = channel.write(buffers);// repeat until all data sent// receiving endlong count = channel.read(buffers);// repeat until all data read?对于浏览器加载页面的过程,由于加载对交互顺序不敏感,所以client可以同时并发多个连接、多个线程并行从服务端获取数据