Design Pattern: Singleton 模式
Singleton的英文意义是独身,也就是只有一个人,应用在物件导向语言上,通常翻译作单例:单一个实例(Instance)。
很多时候,您会需要Singleton模式,例如印表机管理,您希望程式中只能有一个Print Spooler,以避免两个列印动作同时输入至印表机中;例如资料库管理,因为建立连接(Connection)物件会耗用资源,您希望程式中只能有一个连接物件,所有其它的程式都透过这个物件来连接资料库,以避免连接物件的重复开启造成资源的耗用;例如系统程式属性档的读取,您使用单一个物件来读取属性内容,而程式的其它部份都向这个物件要求属性资料,而不是自行读取属性资料。
以印表机设计为例,有的设计人员会采取全域变数的方式来建立实例,并在程式中随机取用这个实例,Java虽然不支援全域变数,但透过将物件包装在一个类别之中,也有人会采用这样的写法:
public class PrintSpooler { public PrintSpooler() { // .... } public Connection getSpooler(){ .... } } public class GlobalObject { private PrintSpooler printSpooler; public GlobalObject () { printSpooler = new PrintSpooler(); ... } public void getPrintSpooler() { return printSpooler; } } public class Runtime { private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime(); public static Runtime getRuntime() { return currentRuntime; } /** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */ private Runtime() {} // 以下略 }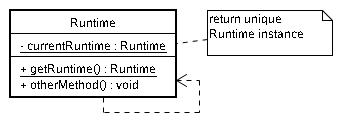
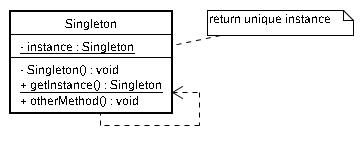
public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = null; private Singleton() { // .... } public static Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; } // .. 其它实作 }Thread1: if(instance == null) // true Thread2: if(instance == null) // true Thread1: instance = new Singleton(); // 产生一个实例 Thread2: instance = new Singleton(); // 又产生一个实例 Thread1: return instance; // 回传一个实例 Thread2: return instance; // 又回传一个实例
public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = null; private Singleton(){} synchronized static public Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; } } public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = null; private Singleton(){} public static Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null){ synchronized(Singleton.class){ if(instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } } } return instance; } } public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); private Singleton() { // .... } public static Singleton getInstance() { return instance; } // 其它实作 }