openstack创建instance的流程
workflow: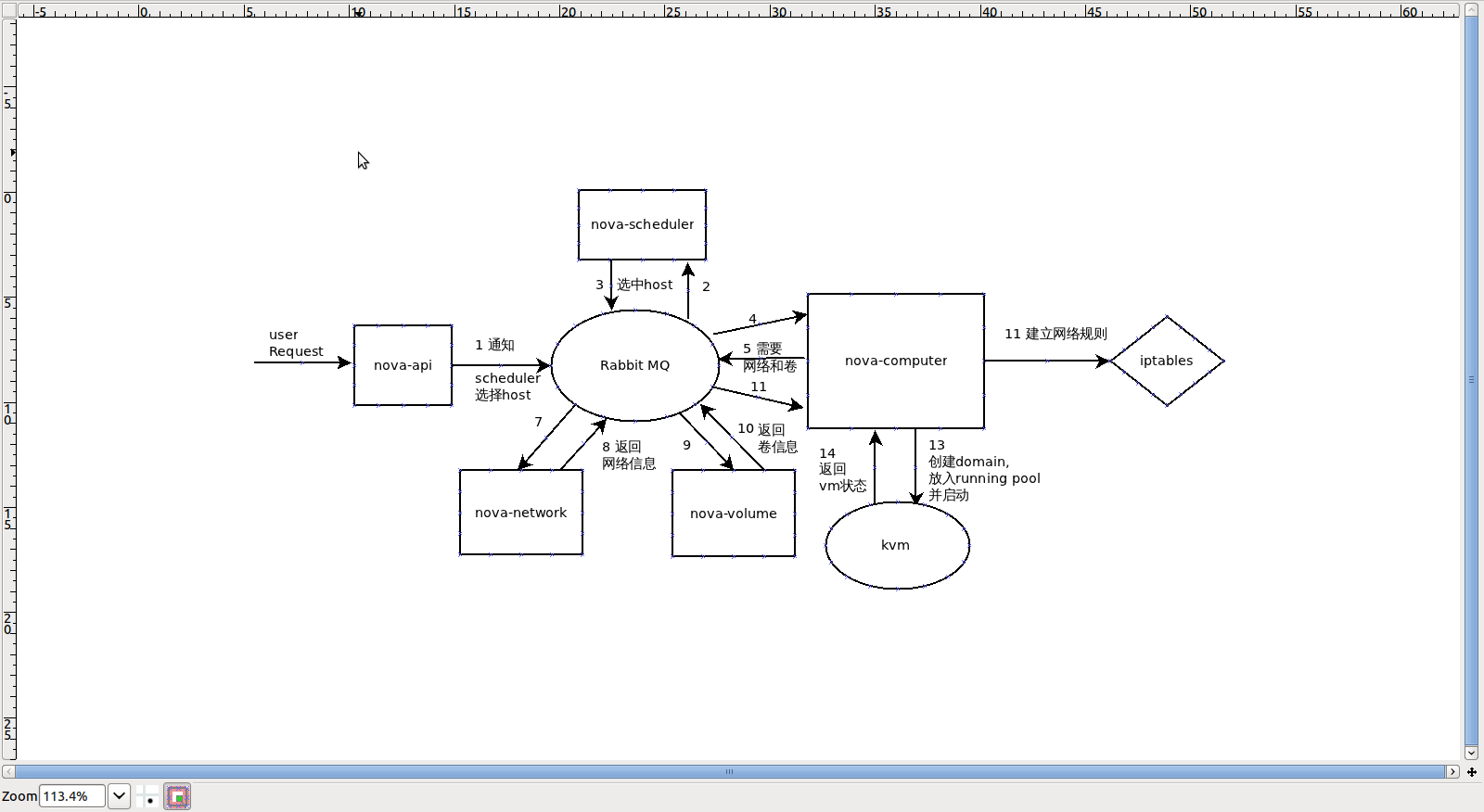
1. 用户向nova-api发送请求
用户发送请求到nova-api,这里有两种:
a.通过openstack api
从 server.py's controller.create():
self.helper.create_instance(req, body, self.compute_api.create)
self._ask_scheduler_to_create_instance(context, base_options, instance_type, zone_blob, availability_zone, injected_files, admin_password, image, instance_id=instance_id, requested_networks=requested_networks)
rpc.cast(context, FLAGS.scheduler_topic, {"method": "run_instance", "args": {"topic": FLAGS.compute_topic, "instance_id": instance_id, "request_spec": request_spec, "availability_zone": availability_zone, "admin_password": admin_password, "injected_files": injected_files, "requested_networks": requested_networks}})def __getattr__(self, key): return functools.partial(self._schedule, key)
def _schedule(self, method, context, topic, *args, **kwargs): ....... rpc.cast(context, db.queue_get_for(context, topic, host), {"method": method, "args": kwargs}) LOG.debug(_("Casted to %(topic)s %(host)s for %(method)s") % locals())network_info = self.network_api.allocate_for_instance(context, instance, vpn=is_vpn, requested_networks=requested_networks)
def allocate_floating_ip(self, context): return rpc.call(context, FLAGS.network_topic, {'method': 'allocate_floating_ip', 'args': {'project_id': context.project_id}}) bd_mapping = self._setup_block_device_mapping(context, instance_id) def create(self, context, size, snapshot_id, name, description, volume_type=None, metadata=None, availability_zone=None): rpc.cast(context, FLAGS.scheduler_topic, {"method": "create_volume", "args": {"topic": FLAGS.volume_topic, "volume_id": volume['id'], "snapshot_id": snapshot_id}})domain = self._create_new_domain(xml) def _create_new_domain(self, xml, persistent=True, launch_flags=0): if persistent: # To create a persistent domain, first define it, then launch it. domain = self._conn.defineXML(xml) domain.createWithFlags(launch_flags) else: # createXML call creates a transient domain domain = self._conn.createXML(xml, launch_flags) return domain
def spawn(self, context, instance, network_info, block_device_info=None): .......... def _wait_for_boot(): instance_name = instance['name'] try: state = self.get_info(instance_name)['state'] except exception.NotFound: msg = _("During reboot, %s disappeared.") % instance_name LOG.error(msg) raise utils.LoopingCallDone if state == power_state.RUNNING: msg = _("Instance %s spawned successfully.") % instance_name LOG.info(msg) raise utils.LoopingCallDone timer = utils.LoopingCall(_wait_for_boot) return timer.start(interval=0.5, now=True)