HDU1325錛欼s It A Tree?
Problem Description
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
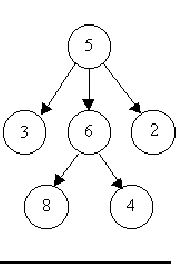
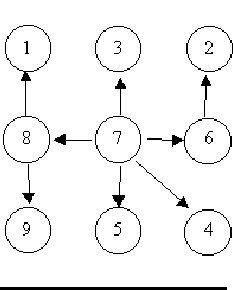
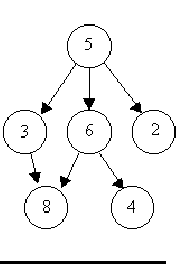
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 45 6 0 08 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 57 4 7 8 7 6 0 03 8 6 8 6 45 3 5 6 5 2 0 0-1 -1
Case 1 is a tree.Case 2 is a tree.Case 3 is not a tree.
//涓?紑濮嬭繕浠ヤ負璺熷皬甯岀殑杩峰鏄竴鏍風殑棰樺憿錛屽悗鏉ユ墠鐭ラ亾杩樻槸鏈夌偣涓嶅悓鐨? =
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int father[100010];int find(int x){ while(father[x] != x) x = father[x]; return x;}int is_father(int m,int n){ while(father[m]!=n) { if(father[m] == m) return 1; m = father[m]; } return 0;}int main(){ int e,flag; int cnt = 0; int big,root,m,n,t; while(~scanf("%d%d",&m,&n) && (m>=0 && n>=0)) { memset(father,0,sizeof(father)); e = 0,flag = 1; root = -1; big = 0; while((m+n)!=0)//m,n閮戒負0鐨勬椂鍊欑粨鏉? { if(e) scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); if(m+n == 0) break; if(big < m)//瀵繪壘鏈?ぇ鐨勯偅涓偣 big = m; if(big < n) big = n; e = 1; if(father[m] == 0) father[m] = m; if(father[n] == 0) father[n] = n; if(father[n]!=n) flag = 0; if(is_father(m,n)) father[n] = m; else flag = 0; } cnt++; printf("Case %d is ",cnt); if(!flag) { printf("not a tree.\n"); continue; } for(int i = 1; i<=big; i++) { if(father[i] == 0) continue; t = find(i); if(t!=root) { if(root == -1) root = t; else { flag = 0; break; } } } if(!flag) { printf("not a tree.\n"); continue; } printf("a tree.\n"); } return 0;}