稀疏矩阵的存储格式(Sparse Matrix Storage Formats)
对于很多元素为零的稀疏矩阵,仅存储非零元素可使矩阵操作效率更高。现有许多种稀疏矩阵的存储方式,但是多数采用相同的基本技术,即存储矩阵所有的非零元素到一个线性数组中,并提供辅助数组来描述原数组中非零元素的位置。
以下是几种常见的稀疏矩阵存储格式:
1. Coordinate Format (COO)
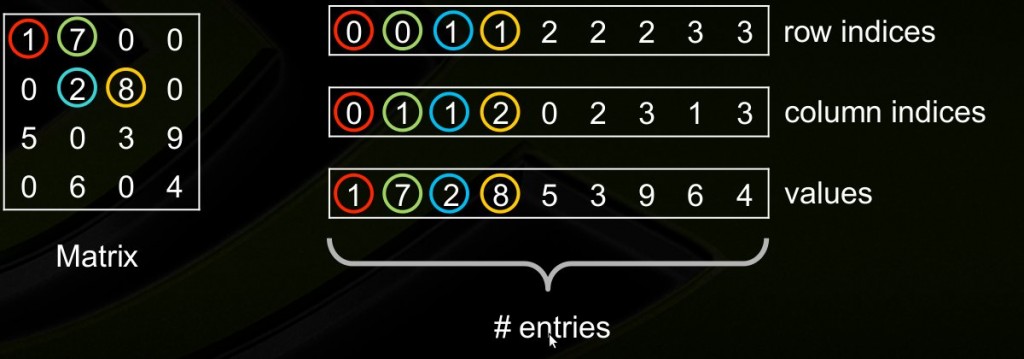
这种存储方式的主要优点是灵活、简单。仅存储非零元素以及每个非零元素的坐标。
使用3个数组进行存储:values, rows, andcolumn
If the sparse matrix has diagonals containing only zero elements, then the diagonal storage format can be used to reduce the amount of information needed to locate the non-zero elements. This storage format is particularly useful in many applications where the matrix arises from a finite element or finite difference discretization.
The Intel MKL diagonal storage format is specified by two arrays:values anddistance, and two parameters:ndiag, which is the number of non-empty diagonals, andlval, which is the declared leading dimension in the calling (sub)programs.?
The Intel MKL compressed sparse row (CSR) format is specified by four arrays: thevalues,columns,pointerB, andpointerE. The following table describes the arrays in terms of the values, row, and column positions of the non-zero elements in a sparse matrixA.
8. Hybrid (HYB)??
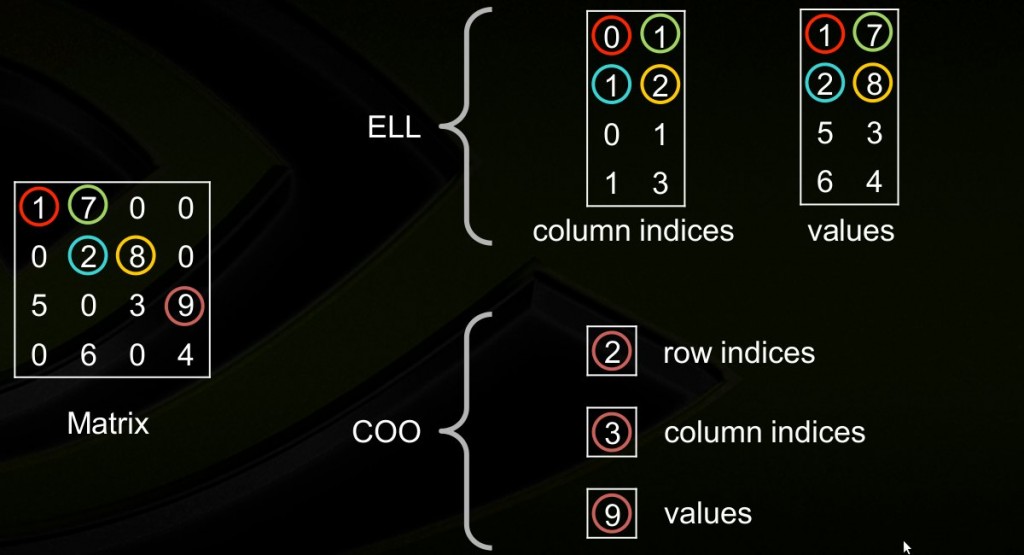
由ELL+COO两种格式结合而成。
选择稀疏矩阵存储格式的一些经验:
1. DIA和ELL格式在进行稀疏矩阵-矢量乘积(sparse matrix-vector products)时效率最高,所以它们是应用迭代法(如共轭梯度法)解稀疏线性系统最快的格式;
2. COO和CSR格式比起DIA和ELL来,更加灵活,易于操作;
3. ELL的优点是快速,而COO优点是灵活,二者结合后的HYB格式是一种不错的稀疏矩阵表示格式;
4. 根据Nathan Bell的工作,CSR格式在存储稀疏矩阵时非零元素平均使用的字节数(Bytes per Nonzero Entry)最为稳定(float类型约为8.5,double类型约为12.5),而DIA格式存储数据的非零元素平均使用的字节数与矩阵类型有较大关 系,适合于StructuredMesh结构的稀疏矩阵(float类型约为4.05,double类型约为8.10),对于Unstructured Mesh以及Random Matrix,DIA格式使用的字节数是CSR格式的十几倍;
5. 从我使用过的一些线性代数计算库来说,COO格式常用于从文件中进行稀疏矩阵的读写,如matrix market即采用COO格式,而CSR格式常用于读入数据后进行稀疏矩阵计算。
?
其他相关链接:
1. Intel MKL 库中使用的稀疏矩阵格式
http://software.intel.com/sites/products/documentation/hpc/mkl/mklman/GUID-9FCEB1C4-670D-4738-81D2-F378013412B0.htm
2. Sparse Matrix Representations & Iterative Solvers, Lesson 1 by Nathan Bell
http://www.bu.edu/pasi/files/2011/01/NathanBell1-10-1000.pdf
欢迎来到我的CSDN博客:http://blog.csdn.net/anshan1984/
?