Java IO--字节流与字符流
1、流的概念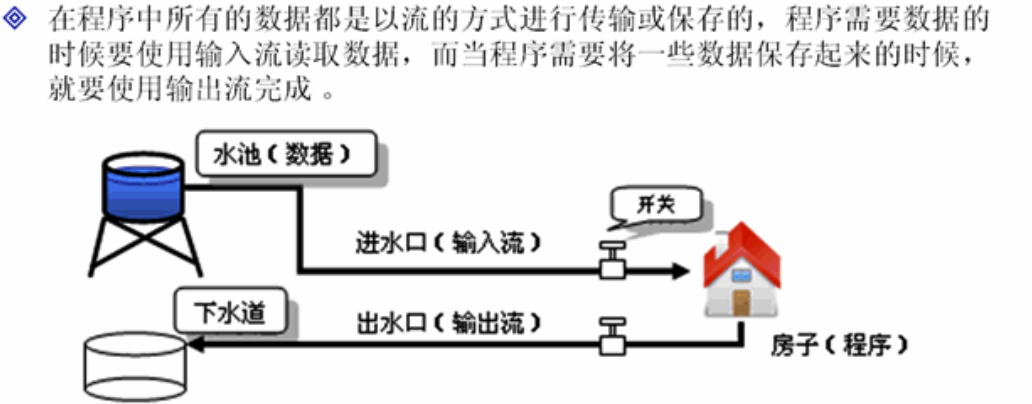
程序中的输入输出都是以流的形式保存的,流中保存的实际上全都是字节文件。
2、字节流与字符流
内容操作就四个类:OutputStream、InputStream、Writer、Reader
3、字节流
3.1字节输出流OutputStream
Clonseable表示可以关闭的操作,因为程序运行到最后肯定要关闭。
Fluashable表示刷新,清空内存中的数据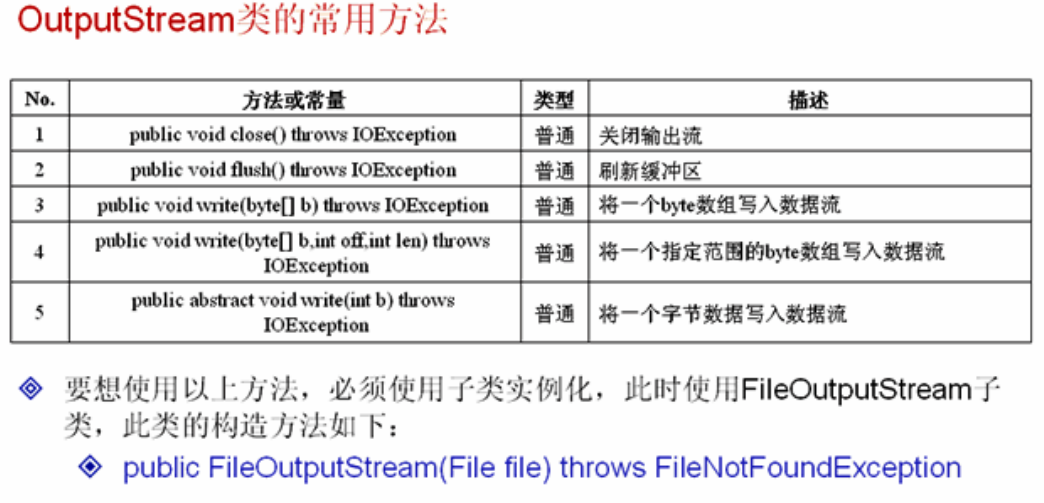
4.1字符输出流Writer
字符流的操作比字节流操作好在一点,就是可以直接输出字符串了。不用再进行转换操作了。
以字符数组的形式读取数据:
验证字符流使用了缓存:6、操作范例import java.io.* ;public class Copy{public static void main(String args[]){if(args.length!=2){// 判断是否是两个参数System.out.println("输入的参数不正确。") ;System.out.println("例:java Copy 源文件路径 目标文件路径") ;System.exit(1) ;// 系统退出}File f1 = new File(args[0]) ;// 源文件的File对象File f2 = new File(args[1]) ;// 目标文件的File对象if(!f1.exists()){System.out.println("源文件不存在!") ;System.exit(1) ;}InputStream input = null ;// 准备好输入流对象,读取源文件OutputStream out = null ;// 准备好输出流对象,写入目标文件try{input = new FileInputStream(f1) ;}catch(FileNotFoundException e){e.printStackTrace() ;}try{out = new FileOutputStream(f2) ;}catch(FileNotFoundException e){e.printStackTrace() ;}if(input!=null && out!=null){// 判断输入或输出是否准备好int temp = 0 ;try{while((temp=input.read())!=-1){// 开始拷贝out.write(temp) ;// 边读边写}System.out.println("拷贝完成!") ;}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace() ;System.out.println("拷贝失败!") ;}try{input.close() ;// 关闭out.close() ;// 关闭}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace() ;}}}}