Java并发系列(五)线程间的通信
Author:Martin
E-mail:mwdnjupt@sina.com.cn
CSDN Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/ictcamera
Sina MicroBlog ID:ITCamera
Main Reference:
《Java并发编程实战》 Brian Goetz etc 童云兰等译
《Java并发设计教程》 温绍锦
线程间的通信的最典型例子就是“生产者-消费者”问题。下面用不同的方式来实现该问题。生产者消费者模型:(很简单)若干个生产者线程向缓存中存放对象,而若干消费者线程从缓存中获取(移除)对象,这个过程要保证操作的一致性。
1. wait-nofity实现线程的wait-nofity方法是Java线程之间基础的交互工具,利用它可以实现 “生产者-消费者问题”,线程的生命周期如下图所示:
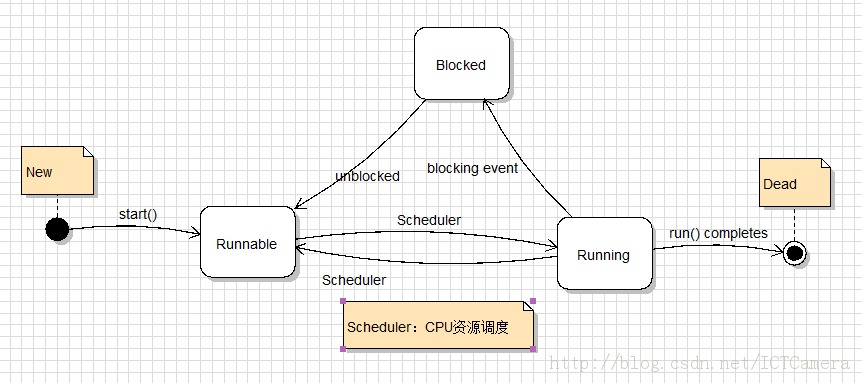
线程生命周期图:引用图片链接 http://www.haogongju.net/art/1835120
代码如下所示:
//货物类public class Item {private static long count=0;private long id=0;private String name;public Item(String name){this.id=++count;this.name=name;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public long getId() {return id;}public String toString(){return "id="+id;}}//仓库类public class Warehouse {private final int MAX_LENGTH=10;private Stack<Item> stack=new Stack<Item>();private boolean isFull=false;private boolean isEmpty=true;public synchronized void produce(Item item){if(isFull){try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}else{ // 为了更清楚的看打印结果,让线程执行慢点,sleep一段时间 try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); e.printStackTrace(); } stack.push(item); System.out.println("Procucer:"+Thread.currentThread().getName() +" procduced:"+item+", current Warehouse="+stack); isFull=stack.size()==MAX_LENGTH; isEmpty=stack.isEmpty(); this.notifyAll();}}public synchronized void cosume(){if(isEmpty){try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}else{ // 为了更清楚的看打印结果,让线程执行慢点,sleep一段时间 try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); e.printStackTrace(); } Item item=stack.pop(); System.out.println("Consumer:"+Thread.currentThread().getName() +" comsumeed:"+item+", current Warehouse="+stack); isFull=stack.size()==MAX_LENGTH; isEmpty=stack.isEmpty(); this.notifyAll();}}}//生产者类public class Productor implements Runnable{ private String name;private Warehouse warehouse=new Warehouse();public Productor (String name,Warehouse warehouse){this.name=name;this.warehouse=warehouse;}public void run() {while (true){Item item=new Item(name);warehouse.produce(item);}}}//消费者类public class Consumer implements Runnable{private String name;private Warehouse warehouse=new Warehouse();public Consumer (String name,Warehouse warehouse){this.name=name;this.warehouse=warehouse;}public void run() {while (true){ warehouse.cosume();}}}//测试类public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Warehouse warehouse=new Warehouse();Thread productor1= new Thread(new Productor("productor1",warehouse),"productor1");Thread productor2= new Thread(new Productor("productor2",warehouse),"productor2");Thread consumer1= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer1",warehouse),"consumer1");Thread consumer2= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer2",warehouse),"consumer2");Thread consumer3= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer3",warehouse),"consumer3"); Thread consumer4= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer4",warehouse),"consumer4"); Thread consumer5= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer5",warehouse),"consumer5"); Thread consumer6= new Thread(new Consumer("consumer6",warehouse),"consumer6");productor1.start(); productor2.start(); consumer1.start(); consumer2.start(); consumer3.start(); consumer4.start(); consumer5.start(); consumer6.start();}}2. 显式锁Lock实现上面的“生产者-消费者”模型也可以用显式锁Lock实现。代码如下:
//仓库类public class BlockQueue<T>{ private static final int MAX_LEN = 5;//假设队列长度为5 private List<T> blockQueue=null;//使用List模拟队列 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition produce = lock.newCondition(); private Condition consume = lock.newCondition(); public BlockQueue(List<T> queue){ blockQueue = queue; } public BlockQueue(){ } public void put(T t) throws InterruptedException{ try{ lock.lock();// 防止两个生产者线程同时进入 if(isFull()) { produce.await();// 生产者等待 } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产者生产了一个数据:" + t); blockQueue.add(t); simulateTimeSpend(); consume.signalAll();// 通知所有的消费者我生产了元素 }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public T take() throws InterruptedException{ T element = null; try{ lock.lock();// 防止两个消费者线程同时进入 if(isEmpty()) { consume.await();// 消费这等待 } simulateTimeSpend(); element = getFirstElement(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 消费者取得数据:" + getValue(element)); produce.signalAll();// 通知 return element; }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } private T getFirstElement(){ // 取队头元素 if(!blockQueue.isEmpty()){ T result=blockQueue.get(0); blockQueue.remove(result); return result; } return null; } public boolean isEmpty(){ return blockQueue.isEmpty(); } public boolean isFull(){ return blockQueue.size()== MAX_LEN; } /** * 模拟生产或者消费要花费一段时间 2013-3-8下午02:35:46 * 推荐随机休眠一段时间 */ private void simulateTimeSpend() { try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public String getValue(T t){ if(t instanceof Integer){ Integer result=(Integer)t; return String.valueOf(result.intValue()); } return t.toString(); }}//生产者类public class Productor implements Runnable{ BlockQueue<Integer> queue ; public Productor(BlockQueue<Integer> queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { while(true) { int data = new Random().nextInt(100000);//产生一个随机数放入 waitMonenet();//随机等待一段时间 try{ queue.put(data); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void waitMonenet() { try{ Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }}//消费者类public class Consumer implements Runnable{ BlockQueue<Integer> queue ; public Consumer(BlockQueue<Integer> queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { while(true) { waitMonenet(); try{ queue.take(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } private void waitMonenet() { try{ Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }}//测试类public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<Integer>(); BlockQueue<Integer> queue = new BlockQueue<Integer>(data); Thread producerA=new Thread(new Productor(queue)); producerA.setName("Producer_A"); Thread producerB=new Thread(new Productor(queue)); producerB.setName("Producer_B"); Thread consumerA=new Thread(new Consumer(queue)); consumerA.setName("Consumer_A"); producerA.start(); producerB.start(); consumerA.start(); }}上面的“生产者-消费者”模型也很容易用并发容器-阻塞队列实现。代码如下:
//货物类public class Item{ //产品序列号 private long id; public Item(long id1) { id = id1; } public long getId() { return id; }}//仓库类public class Warehouse{ //定长阻塞队列 private ArrayBlockingQueue<Item> queue; //通过构造函数传入仓库容量 public Warehouse(int capacity){ queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Item>(capacity); } //向仓库里添加产品,如果仓库已满,等待。。。 public void put(Item pro){ try{ queue.put(pro); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } //从仓库取产品,如果仓库为空,等待。。。 public Item take(){ try{ return queue.take(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return null; }}//生产者类public class Productor implements Runnable{ //产品序列号生成器 private static AtomicLong idManager = new AtomicLong(); //仓库 private Warehouse wareHouse; //通过构造函数传入仓库 public Productor(Warehouse wareHouse1){ wareHouse = wareHouse1; } @Override public void run() { while(true) { //生产一件产品,序列号用 序列号生成器 Item pro = new Item(idManager.getAndIncrement()); //添加到仓库中 wareHouse.put(pro); System.out.println("生产:"+pro.getId()); } }}//消费者类public class Consumer implements Runnable{ //仓库 private Warehouse wareHouse; //通过构造函数传入仓库 public Consumer(Warehouse wareHouse1) { wareHouse = wareHouse1; } @Override public void run() { while(true) { //从仓库取产品 Item pro = wareHouse.take(); System.out.println("消费:"+pro.getId()); } }}//测试类public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { //50个线程 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50); //仓库容量1000 Warehouse warehouse = new Warehouse(1000); //10个生产者 for(int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ;i ++) { pool.execute(new Productor(warehouse)); } //40个消费者 for(int i = 1 ; i <= 40 ;i ++) { pool.execute(new Consumer(warehouse)); } }}