c++编写程序后,出现应用程序错误,指令引用的内存不能“read”
#include <iostream.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50 //注意#define语句后不能用分号。
typedef struct
{
char data[MaxSize];
int length;
}SqList; //L是指向SqList类型的指针变量,同时也是SqList的别名;
void InitList(SqList*& L) //初始化线性表
{
//int * a=new int(10)
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); // L=new (SqList *)(sizeof(SqList));
L->length=0;
}
void DestroyList(SqList* L) //销毁线性表
{
//delete a;
delete L;
}
int ListEmpty(SqList* L) //判断线性表是否为空,注意有返回类型的话,函数类型不能使void类型
{
return(L->length==0);
}
int ListLength(SqList* L) //线性表的长度
{
return L->length;
}
void DisList(SqList* L) //显示线性表中的元素
{
int i;
if(ListEmpty(L))
cout<<"线性表为空"<<endl;
else
for(i=0;i<L->length;i++)
cout<<"线性表为:"<<L->data[i];
cout<<endl;
}
int GetElem(SqList* L,int i,char &e) //获取第i个元素的值,用e返回。注意这里的e要用引用
{
if(i<1||i>L->length)
return 0;
else
e=L->data[i-1];
//return 1;
}
int LocateElem(SqList* L,char e) //获取元素e的位置
{
int i=0; //用i作为返回值;
while(i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) //注意不要写成length,而要写成L->length;
i++; //可不可以用++i?
if(i>=L->length)
return 0;
else
return i+i;
}
int ListInsert(SqList*& L,int i,char e) //在第i个位置上插入一个元素e
{
int j; //为移动做准备,j开始是L->length
if (i<1 || i>L->length+1)
return 0;
i--; //把逻辑位置转换成物理地址,为什么可以用i--;
//else
for(j=L->length;j>i;j--)
L->data[j]=L->data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e;
L->length++; //也用L->length++;
return 1;
/*if(i<1 || i>L->length+1)
return 0;
i=i-1; //把逻辑位置转换成物理地址,为什么可以用i--;
else
for(j=L->L->lenght;j>i;j--)
data[j]=data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e;
L->lenght+1; //也用L->length++;
return 1;*/
}
int ListDelete(SqList*& L,int i,char e)
{
if(i<1 || i>L->length)
return 0;
int j;
i--; //转换为物理地址;
e=L->data[i];
for(j=i+1;j<L->length;j++)
L->data[j-1]=L->data[j];
L->length--;
return 1;
}
void main()
{
SqList* L;
char e,x;
InitList(L);
cout<<"线性表为:";
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++)
for(x='a';x<='z';x++)
ListInsert(L,i,x);
cout<<"e在线性表中的位置为:"<<LocateElem(L,e)<<endl;
cout<<"线性表中第4个元素为:"<< GetElem(L,4,e)<<endl;
cout<<"删除线性表中第2个元素,删除的值为:"<<ListDelete(L,2,e)<<endl;
cout<<"此时的线性表为:";
DisList(L);
cout<<"销毁线性表:";
DestroyList(L);
}
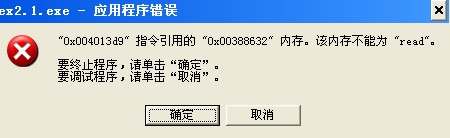
#define MaxSize 50 //这里50
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++)
for(x='a';x<='z';x++)
ListInsert(L,i,x);//这里2层循环远远超过50了,
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 50 //注意#define语句后不能用分号。
typedef struct
{
char data[MaxSize];
int length;
}SqList; //L是指向SqList类型的指针变量,同时也是SqList的别名;
void InitList(SqList*& L) //初始化线性表
{
//int * a=new int(10)
//L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
L = new SqList;//改动
L->length=0;
}
void DestroyList(SqList* L) //销毁线性表
{
//delete a;
delete L;
}
int ListEmpty(SqList* L) //判断线性表是否为空,注意有返回类型的话,函数类型不能使void类型
{
return(L->length==0);
}
int ListLength(SqList* L) //线性表的长度
{
return L->length;
}
void DisList(SqList* L) //显示线性表中的元素
{
int i;
if(ListEmpty(L))
cout<<"线性表为空"<<endl;
else
for(i = 0;i < L->length; i++)
cout<<" "<<L->data[i];
cout<<endl;
}
int GetElem(SqList* L,int i,char &e) //获取第i个元素的值,用e返回。注意这里的e要用引用
{
if(i < 1
[解决办法]
i > L->length)
return 0;
else
e = L->data[i-1];
return 1;
}
int LocateElem(SqList* L,char e) //获取元素e的位置
{
int i=1; //用i作为返回值;
while(i <= L->length && L->data[i-1] != e) //注意不要写成length,而要写成L->length;
i++; //可不可以用++i? (可以)
if(i > L->length)
return 0;
else
return i;
}
int ListInsert(SqList*& L,int i,char e) //在第i个位置上插入一个元素e
{
int j; //为移动做准备,j开始是L->length
if (i < 1
[解决办法]
i >= MaxSize)//L->length 初始化为0,改为i > MaxSize
return 0;
i--; //把逻辑位置转换成物理地址,为什么可以用i--;
for(j = L->length-1; j > i; j--)
L->data[j] = L->data[j-1];
L->data[i] = e;
L->length++; //也用L->length++;
return 1;
/*if(i<1
[解决办法]
i>L->length+1)
return 0;
i=i-1; //把逻辑位置转换成物理地址,为什么可以用i--;
else
for(j=L->L->lenght;j>i;j--)
data[j]=data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e;
L->lenght+1; //也用L->length++;
return 1;*/
}
int ListDelete(SqList*& L,int i,char & e)//y引用
{
if(i < 1
[解决办法]
i > L->length)
return 0;
int j;
i--; //转换为物理地址;
e = L->data[i];
for(j = i+1;j < L->length; j++)
L->data[j-1] = L->data[j];
L->length--;
return 1;
}
int main()
{
SqList* L;
char e = 'e',x = 'a';
InitList(L);
cout<<"线性表为:";
for(int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
ListInsert(L,i,x++);
cout<<"e在线性表中的位置为:"<< LocateElem(L,e) <<endl;
GetElem(L,4,e);
cout<<"线性表中第4个元素为:"<< e <<endl;
ListDelete(L,2,e);
cout << "删除线性表中第2个元素,删除的值为:" << e <<endl;
cout<<"此时的线性表为:";
DisList(L);
cout<<"销毁线性表:";
DestroyList(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 50 //注意#define语句后不能用分号。
typedef struct
{
char data[MaxSize];
int length;
}SqList; //L是指向SqList类型的指针变量,同时也是SqList的别名;
void InitList(SqList*& L) //初始化线性表
{
//int * a=new int(10)
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); // L=new (SqList *)(sizeof(SqList));
L->length=0;
}
void DestroyList(SqList* L) //销毁线性表
{
//delete a;
free(L);
}
int ListEmpty(SqList* L) //判断线性表是否为空,注意有返回类型的话,函数类型不能使void类型
{
return(L->length==0);
}
int ListLength(SqList* L) //线性表的长度
{
return L->length;
}
void DisList(SqList* L) //显示线性表中的元素
{
int i;
if(ListEmpty(L))
cout<<"线性表为空"<<endl;
else
cout<<"线性表为:";
for(i=0;i<L->length;i++)
cout<<L->data[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
char GetElem(SqList* L,int i) //获取第i个元素的值,用e返回。注意这里的e要用引用
{
char e;
if(i<1
[解决办法]
i>L->length)
return 0;
else
e=L->data[i-1];
return e;
}
int LocateElem(SqList* L,char e) //获取元素e的位置
{
int i=0; //用i作为返回值;
while(i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) //注意不要写成length,而要写成L->length;
i++; //可不可以用++i?
if(i>=L->length)
return 0;
else
return i;
}
int ListInsert(SqList* L,int i,char e) //在第i个位置上插入一个元素e
{
int j; //为移动做准备,j开始是L->length
if ( i>L->length && L->length+1>MaxSize){
cout<<"链表已满"<<endl;
return 0;}
i--; //把逻辑位置转换成物理地址,为什么可以用i--;
//else
for(j=L->length;j>i;j--)
L->data[j]=L->data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e;
L->length++; //也用L->length++;
return 1;
}
char ListDelete(SqList*& L,int i,char e)
{
if(i<1
[解决办法]
i>L->length)
return 0;
int j;
i--; //转换为物理地址;
e=L->data[i];
for(j=i+1;j<L->length;j++)
L->data[j-1]=L->data[j];
L->length--;
return e;
}
void main()
{
SqList* L;
char e='x',x;
int i;
InitList(L);
cout<<"向线性表中添加元素"<<endl;
for(x='a', i=1;i<=60;x++,i++)
{
if(!ListInsert(L,i,x))
break;
}
DisList(L);
cout<<e<<"在线性表中的位置为:"<<LocateElem(L,e)<<endl;
cout<<"线性表中第4个元素为:"<< GetElem(L,4)<<endl;
cout<<"删除线性表中第2个元素,删除的值为:"<<ListDelete(L,2,e)<<endl;
cout<<"此时的线性表为:";
DisList(L);
cout<<"销毁线性表:";
DestroyList(L);
system("pause");
}