ASIHTTPRequest类库的简单介绍
1.概述
? ? ? 使用iOS SDK中的HTTP网络请求API,相当的复杂,调用很繁琐,ASIHTTPRequest就是一个对CFNetwork API进行了封装,并且使用起来非常简单的一套API,用Objective-C编写,可以很好的应用在Mac OS X系统和iOS平台的应用程序中。ASIHTTPRequest适用于基本的HTTP请求,和基于REST的服务之间的交互。
?
2.ASIHTTPRequest功能很强大,主要特色如下:? ?在源代码的class文件夹中,copy下面的这些文件到你的ios工程中,如果你不确定那个文件是你需要的,你最好全部拷贝到你的工程中
?
打开Build Phases?tab,展开?Link Binary With Libraries然后点击 + 按钮
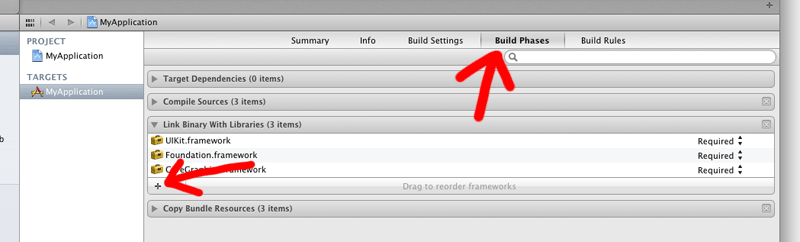
选中?CFNetwork.framework?,然后添加进来
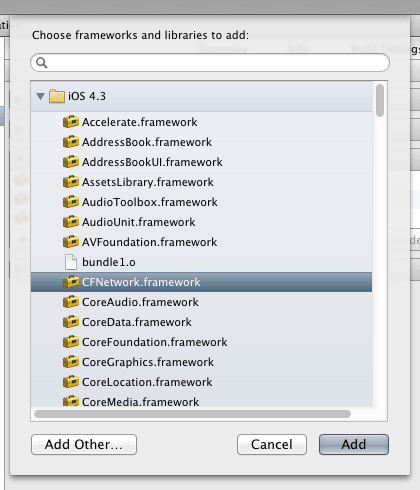
重复上述步骤,依次添加::?SystemConfiguration.framework,?MobileCoreServices.framework,CoreGraphics.framework?and?libz.dylib.
?
?
4.如何使用相应的API?
?
由于篇幅有限,我只在这里简单介绍同步和异步的方法实现,具体文档详见官方地址如下:http://allseeing-i.com/ASIHTTPRequest/,
1)创建的同步请求:
?-(IBAction)grabURL:(id)sender{NSURL*url =[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://allseeing-i.com"]; ASIHTTPRequest*request =[ASIHTTPRequest requestWithURL:url]; [request startSynchronous]; NSError*error =[request error]; if(!error){NSString*response =[request responseString]; }}?
?
?
2)同步请求在实际应用中很少用到,因为同步的话,实际是执行的主线程,如果网络很慢或请求的数据很大,前台界面会一片空白,所以这时候我们往往会采用异步请求数据:
-(IBAction)grabURLInBackground:(id)sender {NSURL*url =[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://allseeing-i.com"]; ASIHTTPRequest*request =[ASIHTTPRequest requestWithURL:url]; [request setDelegate:self]; [request startAsynchronous]; } ? -(void)requestFinished:(ASIHTTPRequest*)request {// Use when fetching text dataNSString*responseString =[request responseString]; ? // Use when fetching binary dataNSData*responseData =[request responseData]; } ? -(void)requestFailed:(ASIHTTPRequest*)request {NSError*error =[request error]; }
3)新版本支持的block
-(IBAction)grabURLInBackground:(id)sender {NSURL*url =[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://allseeing-i.com"]; __block ASIHTTPRequest*request =[ASIHTTPRequest requestWithURL:url]; [request setCompletionBlock:^{// Use when fetching text dataNSString*responseString =[request responseString]; ? // Use when fetching binary dataNSData*responseData =[request responseData]; }]; [request setFailedBlock:^{NSError*error =[request error]; }]; [request startAsynchronous]; }
?
Note the use of the?__block?qualifier when we declare the request, this is important! It tells the block not to retain the request, which is important in preventing a retain-cycle, since the request will always retain the block.
?
?