linux历程间的通信(C): 匿名管道
linux进程间的通信(C): 匿名管道1. Linux进程间的通信简介Linux下的进程通信手段基本上是从Unix平台上的进
linux进程间的通信(C): 匿名管道
1. Linux进程间的通信简介Linux下的进程通信手段基本上是从Unix平台上的进程通信手段继承而来的。
AT&T的贝尔实验室和BSD(加州大学伯克利分校的伯克利软件发布中心)对Unix发展做出重大贡献,但是他们在进程间通信方面的侧重点有所不同。
前者对Unix早期的进程间通信手段进行了系统的改进和扩充,形成了“system V IPC”,但是通信进程局限在单个计算机内;
后者则跳过了单个计算机内限制,形成了基于套接口(socket)的进程间通信机制。Linux则把两者继承了下来。
如下图所示: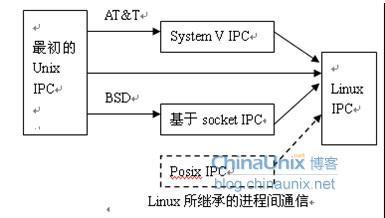 2. 管道管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: A. 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动; B. 需要双工通信时,需要建立起两个管道; C. 只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程之间(具有亲缘关系的进程); D. 单独构成一种独立的文件系统:管道对于管道两端的进程而言,就是一个文件, 但它不是普通的文件,它不属于某种文件系统,而是自立门户, 单独构成一种文件系统,并且只存在与内存中。
2. 管道管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: A. 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动; B. 需要双工通信时,需要建立起两个管道; C. 只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程之间(具有亲缘关系的进程); D. 单独构成一种独立的文件系统:管道对于管道两端的进程而言,就是一个文件, 但它不是普通的文件,它不属于某种文件系统,而是自立门户, 单独构成一种文件系统,并且只存在与内存中。
数据的读出和写入:一个进程向管道中写的内容被管道另一端的进程读出。写入的内容每次都添加在管道缓冲区的末尾,并且每次都是从缓冲区的头部读出数据。
匿名管道的创建:
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int fd[2]);该函数创建的管道的两端处于一个进程中间,在实际应用中没有太大意义;因此,一个进程在由pipe()创建管道后,一般再fork一个子进程,然后通过管道实现父子进程间的通信。因此只要两个进程中存在亲缘关系(这里的亲缘关系指的是具有共同的祖先),都可以采用管道方式来进行通信。
3.匿名管道的读写规则:管道两端可分别用描述字fd[0]以及fd[1]来描述,需要注意的是,管道的两端是固定了任务的。即一端只能用于读,由描述字 fd[0]表示,称其为管道读端;另一端则只能用于写,由描述字fd[1]来表示,称其为管道写端。如果试图从管道写端读取数据,或者向管道读端写入数据 都将导致错误发生。一般文件的I/O函数都可以用于管道,如close、read、write等等。
从管道中读取数据: 如果管道的写端不存在,则认为已经读到了数据的末尾,读函数返回的读出字节数为0; 当管道的写端存在时, 如果请求的字节数目大于PIPE_BUF, 则返回管道中现有数据字节数.
4.示例很多书本或是参考资料讲解进程间通信的例子,通常都只是一个父进程与子进程间的实现,对于实用的启发性不大,
本例是我自己写的一个实现:生成了两个子进程:转换进程和写进程;实现了读取文件,转换成大写,并写输出文件的功能。
父进程不断读文件的数据并通过匿名管道发送到转换进程;转换进程从匿名管道读取数据,转换后,通过匿名管道发送到写进程;写进程从匿名管道读取数据并写到文件。
下面是流程图: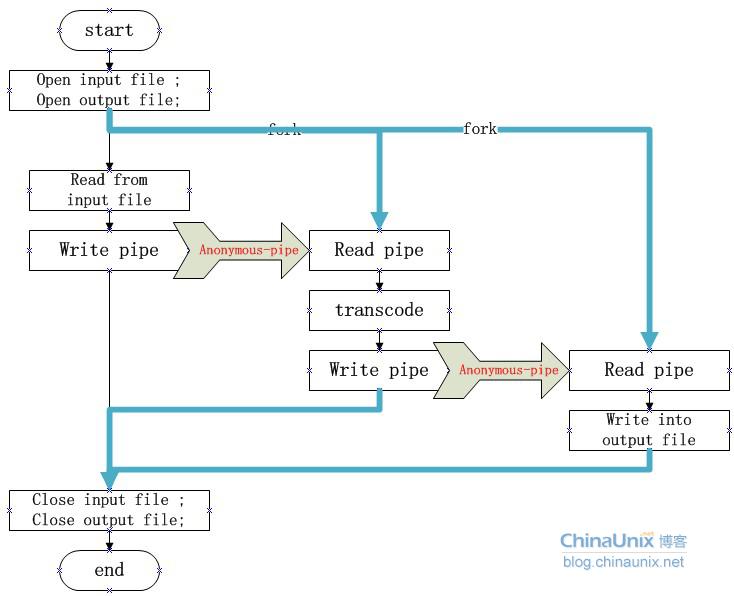
这样的设计是对多进程并行工作的模拟,可以使得读取,转码,写进程实现流水线般的并行,稍作改进,添加功能后,能用在很多的场合。
以下是代码实现:main.c
/*
* \File
* main.c
* \Descript
* father-process reads input file and sends to child-process by anonymous-pipe
* client-process transform and write into output file
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "trans.h"
FILE* fp_in = NULL;
FILE* fp_out = NULL;
#define TESTF_IN "test.dat"
#define TESTF_OUT "out.dat"
#define MAX_LINE 512
#define OP_LEN 100
/*
* \Func
* main
* \Descript
*
*/
int main(char argc, char* argv[])
{
int pidstatus;
int fdfile_in, fdfile_out;
int fdpipe_a[2];
int fdpipe_b[2];
int pid_trans = -1, pid_write = -1;
/* Create anonymous-pipe */
if( (pipe(fdpipe_a) < 0) || (pipe(fdpipe_b) < 0))
{
printf("open pipe failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
if ( (fp_in = fopen(TESTF_IN, "r")) < 0 )
{
printf("open input file failed: %s\n", TESTF_IN);
exit(1);
}
if ( (fp_out = fopen(TESTF_OUT, "w")) < 0 )
{
printf("open input file failed: %s\n", TESTF_OUT);
exit(1);
}
if ( (pid_trans = fork()) && (pid_write = fork()) )
{
/*
* PARENT_PROCESS:
* read data from in-file, write it into anonymos-pipe.
*/
int s_read = 0, s_write;
char bufparent[512];
while((s_read = fread(bufparent, sizeof(char), OP_LEN ,fp_in) ) )
{
printf("***** %d, %s\n", s_read, bufparent);
if ( (s_write = write(fdpipe_a[1], bufparent, s_read)) < 0 )
{
printf("write pipe failed.\n");
exit(1); }
memset(bufparent, 0, 512);
if( feof(fp_in) != 0 )
{
printf("\n***** OVER ******\n");
exit(1);
}
} } else if ( pid_trans == 0 )
{
/*
* TRANS_PROCESS:
* read anonymous-pipe, transcode, write anonymos-pipe.
*/
char buftrans_in[512], buftrans_out[512];
int size_read, size_write;
int ret;
while(size_read = read(fdpipe_a[0], buftrans_in, OP_LEN))
{
ret = trans_lower2upper(buftrans_in, buftrans_out, size_read);
if ( (size_write = write(fdpipe_b[1], buftrans_out, size_read)) < 0 )
{
printf("trans-process write failed.\n");
exit(2); } }
}
else if ( pid_write == 0 )
{
/*
* WRITE_PROCESS:
* read anonymous-pipe, write it into out-file
*/
int s_read, s_write;
char bufwrite[512];
while ( s_read = read(fdpipe_b[0], bufwrite, OP_LEN) )
{
if( (s_write = fwrite(bufwrite, sizeof(char), s_read, fp_out)) < 0)
{
printf("..... write error.\n");
exit(3);
}
if(s_read < OP_LEN)
{
break;
}
}
}
else
{
printf("fork process failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
waitpid(pid_trans, &pidstatus, 0);
waitpid(pid_write, &pidstatus, 0);
fclose(fp_out);
fclose(fp_in);
return 0;
}
trans.h
/*
* \File
* trans.h
* \Descript
*
*/
#ifndef __TRANS_H__
#define __TRANS_H__
int trans_lower2upper(char* buf_in, char* buf_out, int len);
#endif
trans.c
/*
* \File
* trans.c
* \Descript
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "trans.h"
/*
* \Func
* trans_lower2upper
* \Descript
* Lowercase turn uppercase
*/
int trans_lower2upper(char* buf_in, char* buf_out, int buf_len)
{
int len = buf_len;
char* cp_in = buf_in;
char* cp_out = buf_out;
char atom;
char offset;
while(len--)
{
atom = *(cp_in++);
if( (atom >= 'a') && (atom <= 'z') )
{
offset = atom - 'a';
atom = 'A' + offset;
}
*(cp_out++) = atom;
}
return 0;
}
makefile
OBJECTS = main.o trans.o
CC = gcc
anonymous_pipe : $(OBJECTS)
$(CC) -o anonymous_pipe $(OBJECTS)
main.o:trans.h
trans.o:trans.h
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm anonymous_pipe $(OBJECTS)测试通过;
 2. 管道管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: A. 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动; B. 需要双工通信时,需要建立起两个管道; C. 只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程之间(具有亲缘关系的进程); D. 单独构成一种独立的文件系统:管道对于管道两端的进程而言,就是一个文件, 但它不是普通的文件,它不属于某种文件系统,而是自立门户, 单独构成一种文件系统,并且只存在与内存中。
2. 管道管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: A. 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动; B. 需要双工通信时,需要建立起两个管道; C. 只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程之间(具有亲缘关系的进程); D. 单独构成一种独立的文件系统:管道对于管道两端的进程而言,就是一个文件, 但它不是普通的文件,它不属于某种文件系统,而是自立门户, 单独构成一种文件系统,并且只存在与内存中。