总结Spring Security之 关于Authentication
Run-As Manager 和 After-Invocation Manager不重要
The? actual? implementation? of? a? security? interceptor? will? depend? on? what resource is being secured. If you’re securing a URL in a web application, the security? interceptor? will? be? implemented? as? a? servlet? filter.? But? if? you’re? securing? a method invocation, aspects will be used to enforce security.
这篇只说Authentication Manager:
认证是通过AuthenticationManager来管的,
public interface AuthenticationManager {
? public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
????? throws AuthenticationException;
}
The? authenticate()? method? will? attempt? to? authenticate? the? user? using? the org.acegisecurity.Authentication object (which carries the principal and credentials). If successful, the authenticate() method returns a complete Authentication? object,? including? information? about? the? user’s? granted? authorities (which will be considered by the authorization manager).
具体的工作是交给各个 authentication provider来做的:
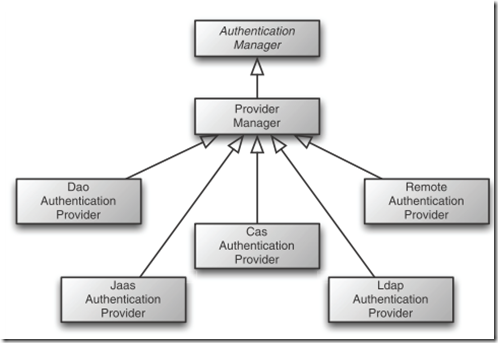
这里provider manager包含多个具体的providers:
<bean id="authenticationManager"
???
??? class="org.acegisecurity.providers.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider">
? <property name="userDetailsService"
????? ref="userDetailsService"/>
</bean>
它会要求一个UserDetailsService, 跟它相关的是UserDetails接口
UserDetailsService接口是个简单的接口
public interface UserDetailsService {
??? UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException, DataAccessException;
}
?
UserDetails接口如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
??? GrantedAuthority[] getAuthorities();
??? String getPassword();
??? String getUsername();
??? boolean isAccountNonExpired();
??? boolean isAccountNonLocked();
??? boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
??? boolean isEnabled();
}
解释一下getAuthorities:该方法返回一个GrantedAuthority[]数组对象,GrantedAuthority是用户权限信息对象,这个对象中定义了一个获取用户权限描述信息的getAuthority()方法。
需要注意Authentication对象才是Spring Security使用的进行安全访问控制用户信息安全对象。实际上,Authentication对象有未认证和已认证两种状态,在作为参数传入认证管理器(AuthenticationManager)的authenticate方法时,是一个未认证的对象,它从客户端获取用户的身份信息(如用户名,密码),可以是从一个登录页面,也可以从Cookie中获取,并由系统自动构造成一个Authentication对象。而这里提到的UserDetails代表一个用户安全信息的源(从数据库,LDAP服务器,CA中心返回),Spring Security要做的就是将这个未认证的Authentication对象和UserDetails进行匹配,成功后将UserDetails中的用户权限信息拷贝到Authentication中组成一个完整的Authentication对象,共其它组件共享。
?
参考:
Spring in Action
Spring Security学习总结: http://www.blogjava.net/redhatlinux/archive/2008/08/20/223148.html
Spring Security2 学习精讲: http://www.iteye.com/topic/319965