I/O的知识储备
背景
前一段时间一直在关注一些nio的相关技术,也和公司的架构师交流了一下,学到了一些相关原理,比如nio的优势和劣势。以及一些排查nio bug问题的方式,受益量多。为自己做一下技术储备,以后可以多玩玩nio的相关技术
知识点unix网络编程第6章: 几种unix下的I/O模型。
?
阻塞I/O模型 ? ?(java io)非阻塞I/O模型I/O复用 ? ? ? ? ?(java 5的nio)信号驱动I/O异步I/O ? ? ? ? ?(java7的aio)几点说明:?1. ?阻塞和非阻塞的概念?? 两者的区别侧重点在于,当前的线程是否会处于挂起,阻塞的状态。2. ?同步和异步的概念?? 两者的区别侧重点在于,是当前业务的处理方式是否是一个串行的过程,异步的操作也可能是阻塞的动作。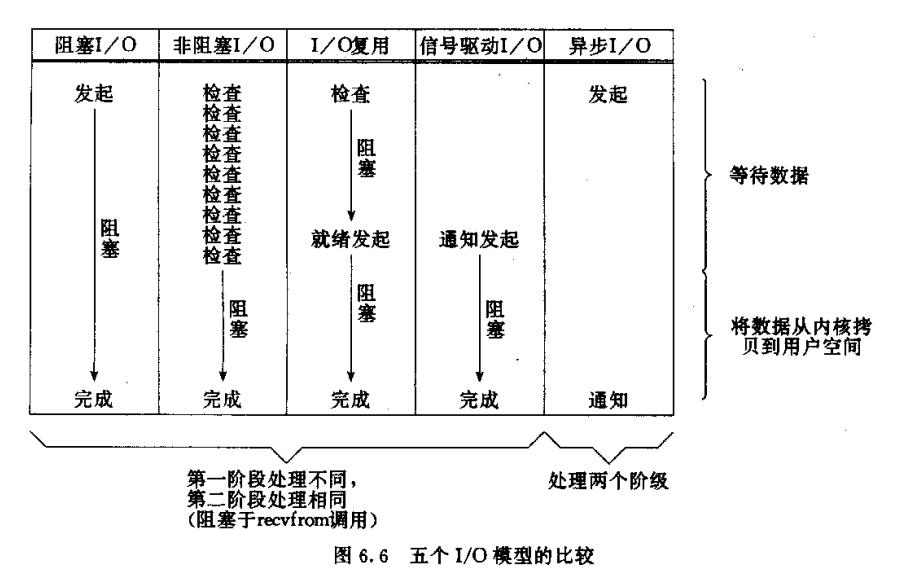
#include<sys/select.h>int select(int maxfdp1, fd_set *restrict readfds, fd_set *restrict writefds,fd_set *restrict exceptfds, struct timeval* restrict tvptr);参数说明: 1. ?最大描述符大小,一般是最大值+1。2. ?中间三个参数readfds、writefds和exceptfds是指向描述符集的指针。这三个描述符集说明了我们关心的可读、可写或出于异常条件的各个描述符。就是一个位表,每次check一下当前描述符在对应位上的值是否为13. ?第4个参数,就是对应的超时参数,精确到微妙,细节我也不关注。
#include <sys/select.h>int pselect(int maxfdp1, fd_set *restrict readfds, fd_set *restrict writefds,fd_set *restrict exceptfds, const struct timespec *restrict tsptr,const sigset_t *restrict sigmask);?
?
它与select的区别在于:??pselect使用timespec结构指定超时值。timespec结构以秒和纳秒表示时间,而非秒和微秒。??pselect的超时值被声明为const,这保证了调用pselect不会改变timespec结构。??pselect可使用一个可选择的信号屏蔽字。在调用pselect时,以原子操作的方式安装该信号屏蔽字,在返回时恢复以前的信号屏蔽字。 多了参数5#include <poll.h>int poll(struct pollfd fdarray[], nfds_t nfds, int timeout);参数说明: 1. pollfd是一个结构体,我们需要关注的描述符
?
struct pollfd { int fd; /* file descriptor to check, or <0 to ignore */ short events; /* events of interest on fd */ short revents; /* events that occurred on fd */};2. nfds代表pollfd的长度
?
返回值:0超时,-1出错, 正数代表准备好的描述符
?
同样变种的有ppoll函数,具体可以见man ppoll,两者的区别和select/pselect区别一样,多了时间精度的支持+信号屏蔽字
?
和select系列的区别点,poll不再受限于select中位数组的长度限制,我们可以将关心的描述符添加到poolfd中。
?
再看epoll函数,是对select/poll的一个增强版:
int epoll_create(int size);int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);1. 第一个参数是epoll_create()的返回值.2. 第二个参数表示动作,用三个宏来表示: EPOLL_CTL_ADD:注册新的fd到epfd中; EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改已经注册的fd的监听事件; EPOLL_CTL_DEL:从epfd中删除一个fd;3. 第三个参数是需要监听的fd4. 第四个参数是告诉内核需要监听什么事events可以是以下几个宏的集合: EPOLLIN :表示对应的文件描述符可以读(包括对端SOCKET正常关闭); EPOLLOUT:表示对应的文件描述符可以写; EPOLLPRI:表示对应的文件描述符有紧急的数据可读(这里应该表示有带外数据到来); EPOLLERR:表示对应的文件描述符发生错误; EPOLLHUP:表示对应的文件描述符被挂断; EPOLLET: 将EPOLL设为边缘触发(Edge Triggered)模式,这是相对于水平触发(Level Triggered)来说的。int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout);1. 等待事件的产生,类似于select()调用。参数events用来从内核得到事件的集合,maxevents告之内核这个events有多大,这个 maxevents的值不能大于创建epoll_create()时的size,2. 参数timeout是超时时间(毫秒,0会立即返回,-1将不确定,也有 说法说是永久阻塞)。该函数返回需要处理的事件数目,如返回0表示已超时。?
?
再看一下jdk中对nio的使用:
?
public static SelectorProvider create() {PrivilegedAction pa = new GetPropertyAction("os.name");String osname = (String) AccessController.doPrivileged(pa); if ("SunOS".equals(osname)) { return new sun.nio.ch.DevPollSelectorProvider(); } // use EPollSelectorProvider for Linux kernels >= 2.6 if ("Linux".equals(osname)) { pa = new GetPropertyAction("os.version"); String osversion = (String) AccessController.doPrivileged(pa); String[] vers = osversion.split("\\.", 0); if (vers.length >= 2) { try { int major = Integer.parseInt(vers[0]); int minor = Integer.parseInt(vers[1]); if (major > 2 || (major == 2 && minor >= 6)) { return new sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorProvider(); } } catch (NumberFormatException x) { // format not recognized } } } return new sun.nio.ch.PollSelectorProvider(); }?
?
比较明显: 如果当前是sunos系统,直接使用DevPoll,在linux 2.6内核下,使用Epoll模型,否则使用Poll。
?
DevPoll估计是sunos自己整的一套poll模型,公司一般使用redhat系列,内核2.6.18,64位主机。所以就介绍下Epoll的实现
?
java实现类: EPollSelectorImpl
?
// wake up使用的两描述符protected int fd0;protected int fd1;// The poll object , native的实现EPollArrayWrapper pollWrapper;// Maps from file descriptors to keys , 文件描述符和SelectKey的关系private HashMap fdToKey;
?
?
看下select()的实现:
PollSelectorImpl类: ==============protected int doSelect(long timeout) //具体执行epoll调用 throws IOException { if (closed) throw new ClosedSelectorException(); processDeregisterQueue(); try { begin(); pollWrapper.poll(timeout); } finally { end(); } processDeregisterQueue(); int numKeysUpdated = updateSelectedKeys(); if (pollWrapper.interrupted()) { // Clear the wakeup pipe pollWrapper.putEventOps(pollWrapper.interruptedIndex(), 0); synchronized (interruptLock) { pollWrapper.clearInterrupted(); IOUtil.drain(fd0); interruptTriggered = false; } } return numKeysUpdated; }继续看下EPollArrayWrappe : ========================== int poll(long timeout) throws IOException { updateRegistrations(); updated = epollWait(pollArrayAddress, NUM_EPOLLEVENTS, timeout, epfd); for (int i=0; i<updated; i++) { // 这里判断下当前响应的描述符是否为fd0,后面再细说 if (getDescriptor(i) == incomingInterruptFD) { interruptedIndex = i; interrupted = true; break; } } return updated; }继续看下EPollArrayWrapper 的native实现: epollWait(): ?====================JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_sun_nio_ch_EPollArrayWrapper_epollWait(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jlong address, jint numfds, jlong timeout, jint epfd){ struct epoll_event *events = jlong_to_ptr(address); int res; if (timeout <= 0) { /* Indefinite or no wait */ RESTARTABLE((*epoll_wait_func)(epfd, events, numfds, timeout), res); } else { /* Bounded wait; bounded restarts */ res = iepoll(epfd, events, numfds, timeout); } if (res < 0) { JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "epoll_wait failed"); } return res;}static int iepoll(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int numfds, jlong timeout) { jlong start, now; int remaining = timeout; struct timeval t; int diff; gettimeofday(&t, NULL); start = t.tv_sec * 1000 + t.tv_usec / 1000; //转化为ns单位 for (;;) { int res = (*epoll_wait_func)(epfd, events, numfds, timeout); if (res < 0 && errno == EINTR) { //处理异常 if (remaining >= 0) { gettimeofday(&t, NULL); now = t.tv_sec * 1000 + t.tv_usec / 1000; diff = now - start; remaining -= diff; if (diff < 0 || remaining <= 0) { return 0; } start = now; } } else { return res; } }}?
看下wakeup的实现 :?
?
EPollSelectorImpl类: EPollSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) {super(sp); int[] fdes = new int[2]; IOUtil.initPipe(fdes, false); fd0 = fdes[0]; fd1 = fdes[1]; pollWrapper = new EPollArrayWrapper(); pollWrapper.initInterrupt(fd0, fd1); // 设置中断的两个描述符 fdToKey = new HashMap(); } public Selector wakeup() { synchronized (interruptLock) { if (!interruptTriggered) { pollWrapper.interrupt(); //调用warpper进行中断 interruptTriggered = true; } }return this; }继续看下EPollArrayWrapper : void initInterrupt(int fd0, int fd1) { outgoingInterruptFD = fd1; //保存pipeline的描述符 incomingInterruptFD = fd0; epollCtl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd0, EPOLLIN); //注册到epoll上。 } public void interrupt() { interrupt(outgoingInterruptFD); //调用native方法 } 继续看下EPollArrayWrapper.c native实现: JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_sun_nio_ch_EPollArrayWrapper_interrupt(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jint fd){ int fakebuf[1]; fakebuf[0] = 1; if (write(fd, fakebuf, 1) < 0) { //发送一字节的内容,让epoll_wait()能得到及时响应 JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env,"write to interrupt fd failed"); }}?实现方式也是挺简单的,弄了两个fd,一个往另一个写1byte的内容,促使epoll_wait能得到响应。
?
异步I/O模型:
?
暂时还未真实用过,只是大致看过其api,有兴趣可以自己baidu。?
?
?
?
后续会起一篇,单独针对nio在服务端和客户端使用上的注意点,主要是吸收了一些大牛门的经验,需要做个总结,消化一下。