抉择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲
选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲本文内容框架:§1 选择排序§2 锦
选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲
选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲
本文内容框架:
§1 选择排序
§2 锦标赛排序
§3 堆排序
§4 Smooth Sort
§5 小结
§1 选择排序
选择排序(Selection sort)
选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理如下。首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕。下图能够帮助很直观的理解出选择排序算法的思想:

二叉堆是完全二叉树或者是近似完全二叉树。
二叉堆满足二个特性:
1.父结点的键值总是大于或等于(小于或等于)任何一个子节点的键值。
2.每个结点的左子树和右子树都是一个二叉堆(都是最大堆或最小堆)。
当父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆。当父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最小堆。下图展示一个最小堆:
堆的存储
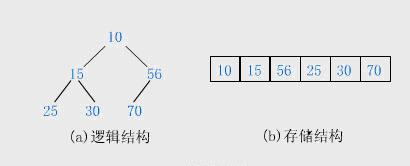
一般都用数组来表示堆,i结点的父结点下标就为(i – 1) / 2。它的左右子结点下标分别为2 * i + 1和2 * i + 2。如第0个结点左右子结点下标分别为1和2。
在堆的数据结构中,堆中的最大值总是位于根节点。堆中定义以下几种操作:
最大堆调整(Max_Heapify):将堆的末端子结点作调整,使得子结点永远小于父结点
创建最大堆(Build_Max_Heap):将堆所有数据重新排序
堆排序(HeapSort):移除位在第一个数据的根结点,并做最大堆调整的递归运算
§4 Smooth Sort
Smooth Sort算法
Smooth Sort基本思想和Heap Sort相同,但Smooth Sort使用的是一种由多个堆组成的优先队列,这种优先队列在取出最大元素后剩余元素可以就地调整成优先队列,所以Smooth Sort不用像Heap Sort那样反向地构建堆,在数据基本有序时可以达到O(n)复杂度。Smooth Sort算法在维基百科上有详细介绍。
Smooth Sort是所有算法中时间复杂度理论值最好的,但由于Smooth Sort所用的优先队列是基于一种不平衡的结构,复杂度因子很大,所以该算法的实际效率并不是很好。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> static unsigned int set_times = 0; static unsigned int cmp_times = 0; template<typename item_type> void setval(item_type& item1, item_type& item2) { set_times += 1; item1 = item2; return; } template<typename item_type> int compare(item_type& item1, item_type& item2) { cmp_times += 1; return item1 < item2; } template<typename item_type> void swap(item_type& item1, item_type& item2) { item_type item3; setval(item3, item1); setval(item1, item2); setval(item2, item3); return; } static const unsigned int leonardo[] = { 1, 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 25, 41, 67, 109, 177, 287, 465, 753, 1219, 1973, 3193, 5167, 8361, 13529, 21891, 35421, 57313, 92735, 150049, 242785, 392835, 635621, 1028457, 1664079, 2692537, 4356617, 7049155, 11405773, 18454929, 29860703, 48315633, 78176337, 126491971, 204668309, 331160281, 535828591, 866988873, 1402817465, 2269806339u, 3672623805u, }; template<typename item_type> inline void smooth_sort_fix( item_type* array, int current_heap, int level_index, int* levels) { int prev_heap; int max_child; int child_heap1; int child_heap2; int current_level; while(level_index > 0) { prev_heap = current_heap - leonardo[levels[level_index]]; if(compare(array[current_heap], array[prev_heap])) { if(levels[level_index] > 1) { child_heap1 = current_heap - 1 - leonardo[levels[level_index] - 2]; child_heap2 = current_heap - 1; if(compare(array[prev_heap], array[child_heap1])) break; if(compare(array[prev_heap], array[child_heap2])) break; } swap(array[current_heap], array[prev_heap]); current_heap = prev_heap; level_index -= 1; } else break; } current_level = levels[level_index]; while(current_level > 1) { max_child = current_heap; child_heap1 = current_heap - 1 - leonardo[current_level - 2]; child_heap2 = current_heap - 1; if(compare(array[max_child], array[child_heap1])) max_child = child_heap1; if(compare(array[max_child], array[child_heap2])) max_child = child_heap2; if(max_child == child_heap1) { swap(array[current_heap], array[child_heap1]); current_heap = child_heap1; current_level -= 1; } else if(max_child == child_heap2) { swap(array[current_heap], array[child_heap2]); current_heap = child_heap2; current_level -= 2; } else break; } return; } template<typename item_type> void smooth_sort(item_type* array, int size) { int levels[64] = {1}; int toplevel = 0; int i; for(i = 1; i < size; i++) { if(toplevel > 0 && levels[toplevel - 1] - levels[toplevel] == 1) { toplevel -= 1; levels[toplevel] += 1; } else if(levels[toplevel] != 1) { toplevel += 1; levels[toplevel] = 1; } else { toplevel += 1; levels[toplevel] = 0; } smooth_sort_fix(array, i, toplevel, levels); } for(i = size - 2; i > 0; i--) { if(levels[toplevel] <= 1) { toplevel -= 1; } else { levels[toplevel] -= 1; levels[toplevel + 1] = levels[toplevel] - 1; toplevel += 1; smooth_sort_fix(array, i - leonardo[levels[toplevel]], toplevel - 1, levels); smooth_sort_fix(array, i, toplevel, levels); } } return; } int main(int argc, char** argv) { int capacity = 0; int size = 0; int i; clock_t clock1; clock_t clock2; double data; double* array = NULL; // generate randomized test case while(scanf("%lf", &data) == 1) { if(size == capacity) { capacity = (size + 1) * 2; array = (double*)realloc(array, capacity * sizeof(double)); } array[size++] = data; } // sort clock1 = clock(); smooth_sort(array, size); clock2 = clock(); // output test result fprintf(stderr, "smooth_sort:\t"); fprintf(stderr, "time %.2lf\t", (double)(clock2 - clock1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); fprintf(stderr, "cmp_per_elem %.2lf\t", (double)cmp_times / size); fprintf(stderr, "set_per_elem %.2lf\n", (double)set_times / size); for(i = 0; i < size; i++) { fprintf(stdout, "%lf\n", array[i]); } free(array); return 0; }
§5 小结
这篇博文列举了选择排序的几个算法,管中窥豹,不求甚解。如果你有任何建议或者批评和补充,请留言指出,不胜感激,更多参考请移步互联网。
参考:
①MoreWindows:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6709644
②RichSelian:http://www.cnblogs.com/richselian/archive/2011/09/16/2179148.html
③kapinter:http://zdker.blog.163.com/blog/static/584834200659636560/
④更多参考来着维基百科


