分布排序(distribution sorts)算法大串讲
分布排序(distribution sorts)算法大串讲
本文内容框架:
§1 鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole)
§2 桶排序(Bucket Sort)
§3 基数排序(Radix Sort)
§4 计数排序(Counting Sort)
§5 Proxmap Sort
§6 珠排序(Bead Sort)
§7 小结
本文介绍的排序算法是基于分配、收集的排序算法,分配排序的基本思想:排序过程无须比较关键字,而是通过"分配"和"收集"过程来实现排序.它们的时间复杂度可达到线性阶:O(n)。不受比较排序算法时间复杂度O(nlogn)的下限限制。
§1 鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole)
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort)
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort),也被称作基数分类, 是一种时间复杂度为O(n)且在不可避免遍历每一个元素并且排序的情况下效率最好的一种排序算法。但它只有在差值(或者可被映射在差值)很小的范围内的数值排序的情况下实用,同时也要求元素个数(n)和成为索引的值(N)大小相当。
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort)算法的时间复杂度都是O(N+n),空间复杂度是O(N)。
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort)算法的思想就是使用一个辅助数组,这个辅助数组的下标对应要排序数组的元素值即使用辅助数组的下标进行排序,辅助数组元素的值记录该下标元素值的在要排序数组中的个数。
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort)算法步骤:
1.对于给定的一组要排序的数组,需要初始化一个空的辅助数组(“鸽巢”),把初始数组中的每个值作为一个key(“鸽巢”)即辅助数组的索引即是待排序数组的值。
2.遍历初始数组,根据每个值放入辅助数组对应的“鸽巢”
3.顺序遍历辅助数组,把辅助数组“鸽巢”中不为空的数放回初始数组中
鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole sort)算法实现举例
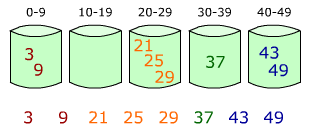
1、箱排序的基本思想
箱排序也称桶排序(Bucket Sort),其基本思想是:设置若干个箱子,依次扫描待排序的记录R[0],R[1],…,R[n-1],把关键字等于k的记录全都装入到第k个箱子里(分配),然后按序号依次将各非空的箱子首尾连接起来(收集)。
【例】要将一副混洗的52张扑克牌按点数A<2<…<J<Q<K排序,需设置13个"箱子",排序时依次将每张牌按点数放入相应的箱子里,然后依次将这些箱子首尾相接,就得到了按点数递增序排列的一副牌。
2、箱排序中,箱子的个数取决于关键字的取值范围。
若R[0..n-1]中关键字的取值范围是0到m-1的整数,则必须设置m个箱子。因此箱排序要求关键字的类型是有限类型,否则可能要无限个箱子。
3、箱子的类型应设计成链表为宜
一般情况下每个箱子中存放多少个关键字相同的记录是无法预料的,故箱子的类型应设计成链表为宜。
4、为保证排序是稳定的,分配过程中装箱及收集过程中的连接必须按先进先出原则进行。
(1) 实现方法一
每个箱子设为一个链队列。当一记录装入某箱子时,应做人队操作将其插入该箱子尾部;而收集过程则是对箱子做出队操作,依次将出队的记录放到输出序列中。
(2) 实现方法二
若输入的待排序记录是以链表形式给出时,出队操作可简化为是将整个箱子链表链接到输出链表的尾部。这只需要修改输出链表的尾结点中的指针域,令其指向箱子链表的头,然后修改输出链表的尾指针,令其指向箱子链表的尾即可。
桶排序算法实现举例
若这d个分量中每个分量都是一个独立的关键字,则文件是多关键字的(如扑克牌有两个关键字:点数和花色);否则文件是单关键字的,
![]() (0≤j<d)只不过是关键字中其中的一位(如字符串、十进制整数等)。
(0≤j<d)只不过是关键字中其中的一位(如字符串、十进制整数等)。
多关键字中的每个关键字的取值范围一般不同。如扑克牌的花色取值只有4种,而点数则有13种。单关键字中的每位一般取值范围相同。
2、基数
设单关键字的每个分量的取值范围均是:
C0≤kj≤Crd-1(0≤j<d)
可能的取值个数rd称为基数。
基数的选择和关键字的分解因关键宇的类型而异:
(1) 若关键字是十进制整数,则按个、十等位进行分解,基数rd=10,C0=0,C9=9,d为最长整数的位数;
(2) 若关键字是小写的英文字符串,则rd=26,Co='a',C25='z',d为字符串的最大长度。
3、基数排序的基本思想
基数排序的基本思想是:从低位到高位依次对Kj(j=d-1,d-2,…,0)进行箱排序。在d趟箱排序中,所需的箱子数就是基数rd,这就是"基数排序"名称的由来。
基数排序的时间复杂度是 O(k·n),其中n是排序元素个数,k是数字位数。注意这不是说这个时间复杂度一定优于O(n·log(n)),因为k的大小一般会受到 n 的影响。基数排序所需的辅助存储空间为O(n+rd)。
基数排序的方式可以采用LSD(Least significant digital)或MSD(Most significant digital),LSD的排序方式由键值的最右边开始,而MSD则相反,由键值的最左边开始。
基数排序算法实现举例
计数排序算法实现举例
Technique:
/* Map all integer keys to floats in range 0<= Key < 1 */ KeyFloat = KeyInt / (1 + MAXKEYINTVALUE); /* Map all float keys to indices in range 0<= Index < ARRAYSIZE */ Index = floor(ARRAYSIZE * KeyFloat);
RunningTotal = 0; /* Init counter */ for(i=0; i 0) /* There were hits at this address */ { ProxMap[i] = RunningTotal; /* Set start index for this set */ RunningTotal += HitList[i]; } }Move keys from the unsorted array to the sorted array using an insertion sort technique for each bucket.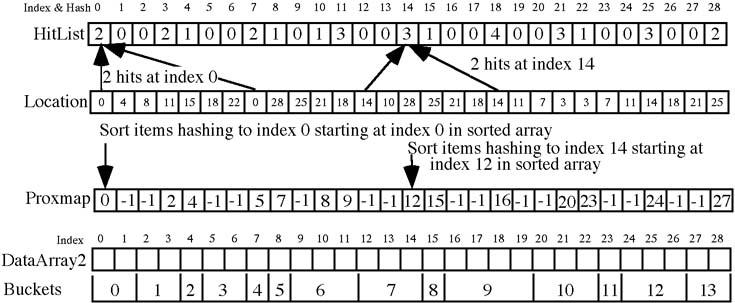
Analysis: ProxMap sorting runs in a surprisingly fast O(n) time.
图1
上图1中的三个珠就表示数字3,两个珠表示数字2。

图2
图2(a)中有两个数字,4和3,分别串在四条线上,于是数字 4的最后一个珠子下落,因为它下边是空的,自由下落后变成图2(b),图2(c)中随机给了四个数字,分别是3,2,4,2,这些珠子自由下落,就变成了 (d)中,落完就有序了,2,2,3,4,以上就是珠排序的精华。
珠排序算法的图很像之前介绍过的跳跃表(Skip List)的结构。
§7 小结
这篇博文列举了选择排序的6个算法,基本可以掌握其中概要,管中窥豹,不求甚解。如果你有任何建议或者批评和补充,请留言指出,不胜感激,更多参考请移步互联网。
参考:
①awsqsh:http://blog.csdn.net/awsqsh/article/details/6133562
②数据结构自考网: http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/paixu/paixu8.6.1.1.htm
③juvenfan:http://www.cnblogs.com/juventus/archive/2012/06/06/2538834.html
④Gossip@caterpillar:http://caterpillar.onlyfun.net/Gossip/AlgorithmGossip/RadixSort.htm
⑤数据结构自考网: http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/paixu/paixu8.6.2.htm
⑥NeilHappy:http://blog.csdn.net/neilhappy/article/details/7202507
⑦kkun:http://www.cnblogs.com/kkun/archive/2011/11/23/2260301.html
⑧Promap Sort: http://www.cs.uah.edu/~rcoleman/CS221/Sorting/ProxMapSort.html