赵雅智_Java 反射
一个类有多个组成部分,例如:成员变量,方法,构造方法等。
反射就是加载类,并解剖出类的各个组成部分。
java反射机制提供的功能:
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类在运行时构造任意一个类的对象在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法。包括private的方法生成动态代理Java反射所需要的类并不多,主要有java.lang.Class类和java.lang.reflect包中的Field、Constructor、Method、Array类。
class类:类和接口
Field类:字段
Constructor类:构造方法
Method类:方法
Array类:数组
注意:
Class类是Java反射的起源,针对任何一个你想探勘的类,只有先为它产生一个Class类的对象,接下来才能通过Class对象获取其他想要的信息。
class类:
JVM为每种类型管理着一个独一无二的Class对象----每个类(型)都有一个Class对象。系统对所有对象进行的运行时类型标识---->Class类对象用来保存这些类型信息的。Java程序运行过程中,当需要创建某个类的实例时,JVM首先检查所要加载的类对应的Class对象是否已经存在。
如果还不存在,JVM就会根据类名查找对应的字节码文件并加载,接着创建对应的Class对象,最后才创建出这个类的实例。
例如,
Java基本数据类型(boolean、byte、char、short、int、long、float 和 double);
关键字void 也都对应一个 Class 对象;
每个数组属性也被映射为 Class 对象,所有具有相同类型和维数的数组都共享该 Class 对象。
因此,运行中的类或接口在JVM中都会有一个对应的Class对象存在,它保存了对应类或接口的类型信息。要想获取类或接口的相应信息,需要先获取这个Class对象。
获得class类对象
Java中有一个Class类用于代表某一个类的字节码。使用Class类的forName()静态方法获得与字符串对应的Class对象参数字符串必须是类或接口的完全限定名Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.String");类名.classClass c1 = Manager.class;Class c2 = int.class;//intClass c3 = Integer,class;//java.lang.IntegerClass c4 = double[].class;对象.getClass()
MyObject x = new MyObject();Class c1 = x.getClass();
Class对象提供了如下常用方法:
public String getName():获取Class对象所表示实体的完全限定名public Field[] getField():所有public字段Public Constructor getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) :所有public构造方法Public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes):所有public方法public Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes):所有的构造方法public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class... parameterTypes):所有的方法public Field getDeclaredField(String name) :所有的字段这些方法分别用于从类中解剖出构造函数、方法和成员变量(属性)。解剖出的成员分别使用Constructor、 Method 、 Field 对象表示。
构造方法:
Constructor类提供了如下方法,用于创建类的对象:
public Object newInstance(Object... initargs)
initargs用于指定构造函数接收的参数
sun公司为简化开发人员创建对象,它在class对象中也提供了一个newInstance方法,用于创建类的对象。
这样开发人员可以避免每次都需要去反射Constructor 类以创建对象。
不过需要注意的是:
class.newInstance方法内部是反射类无参的构造函数创建的对象,所以利用此种方式创建类对象时,类必须有一个无参的构造函数。
练习:反射类无参、有参、私有的构造函数,创建类的对象。
package com.hbsi.reflect;public class Person {public String sex="nan";public String getSex() {return sex;}public void setSex(String sex) {this.sex = sex;}private String name="zhangsan";private int age;public Person(){//System.out.println("无参构造");}public Person(String name){//this.name=name;System.out.println(name);}public Person(String name,int age){System.out.println(name+"..."+age);}private Person(int age){System.out.println("私有");}public void run(){System.out.println("run...");}public void run(String name){System.out.println("run..."+name);}public void run(String name,int age){System.out.println("run..."+name+"..."+age);}public int sum(int i,int j){return i+j;}private void sum1(){System.out.println("sum1...");}public static void sum2(){System.out.println("sum2...");}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}}package com.hbsi.reflect;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import org.junit.Test;public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {Demo2 d = new Demo2();d.test1();System.out.println("-----");d.test2();System.out.println("-----");d.test3();System.out.println("-----");d.test4();System.out.println("-----");d.test5();}//反射出无参的构造方法,并创建一个person对象@Testpublic void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{//加载类Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");//反射出构造方法Constructor c=clazz.getConstructor(null);Person p=(Person)c.newInstance(null);System.out.println(p.getName());}//反射出 public Person(String name)@Testpublic void test2() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{//加载类Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");//反射出构造方法Constructor c=clazz.getConstructor(String.class);Person p=(Person)c.newInstance("lisi");System.out.println(p.getName());}//反射出public Person(String name,int age)@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{//加载类Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");//反射出构造方法Constructor c=clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);Person p=(Person)c.newInstance("lisi",23);System.out.println(p.getName());}//反射private Person(int age)@Testpublic void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{//加载类Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");//反射出构造方法Constructor c=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);c.setAccessible(true); //如果是private的,必须设置访问权限Person p=(Person)c.newInstance(24);System.out.println(p.getName());}@Testpublic void test5() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {//加载类Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Person p=(Person)clazz.newInstance();System.out.println(p.getName());}}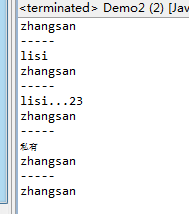
方法:
Method对象提供了如下方法,用于执行它所代表的方法:
public Object invoke(Object obj,Object... args)
练习:使用Method分别执行无参、有参、多个参(带数组和基本数据类型)、静态、私有的方法。
package com.hbsi.reflect;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import org.junit.Test;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {Demo3 d = new Demo3();d.test1();System.out.println("-----");d.test2();System.out.println("-----");d.test3();System.out.println("-----");d.test4();System.out.println("-----");d.test5();}// public void run()@Testpublic void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{Person p=new Person();Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Method m=clazz.getMethod("run",null);m.invoke(p,null);}//public void run(String name)@Testpublic void test2() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{Person p=new Person();Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Method m=clazz.getMethod("run",String.class);m.invoke(p,"zhangsan");}//public int sum(int i,int j)@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{Person p=new Person();Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Method m=clazz.getMethod("sum",int.class,int.class);int value=(Integer)m.invoke(p,12,2);System.out.println(value);}//private void sum1()@Testpublic void test4() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{Person p=new Person();Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Method m=clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sum1",null);m.setAccessible(true);m.invoke(p,null);}//public static void sum2()@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Testpublic void test5() throws ClassNotFoundException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException{//Person p=new Person();Class clazz=Class.forName("com.hbsi.reflect.Person");Method m=clazz.getMethod("sum2",null);m.invoke(null,null);}}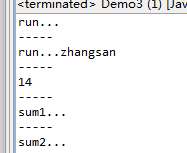
jdk1.4和jdk1.5的invoke方法的区别:
Jdk1.5:public Object invoke(Object obj,Object... args)
Jdk1.4:public Object invoke(Object obj,Object[] args),
问题:
启动Java程序的main方法的参数是一个字符串数组,即public static void main(String[] args),通过反射方式来调用这个main方法时,如何为invoke方法传递参数呢?按jdk1.5的语法,整个数组是一个参数,而按jdk1.4的语法,数组中的每个元素对应一个参数,当把一个字符串数组作为参数传递给invoke方法时,javac会到底按照哪种语法进行处理呢?jdk1.5肯定要兼容jdk1.4的语法,会按jdk1.4的语法进行处理,即把数组打散成为若干个单独的参数。所以,在给main方法传递参数时,不能使用代码mainMethod.invoke(null,new String[]{“xxx”}),javac只把它当作jdk1.4的语法进行理解,而不把它当作jdk1.5的语法解释,因此会出现参数类型不对的问题。
解决办法:
mainMethod.invoke(null,new Object[]{new String[]{"xxx"}});
mainMethod.invoke(null,(Object)new String[]{"xxx"});
编译器会作特殊处理,编译时不把参数当作数组看待,也就不会数组打散成若干个参数了
字段:
Field对象提供了如下方法,用于设置、获取对象属性的值:
public void set(Object obj,Object value)
public Object get(Object obj)
练习:利用Field分别设置和获取公有、私有的属性。
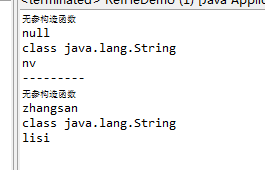
package net.csdn.high;import java.util.Date;public class Student {private String name = "zhangsan";private int age;private Date birthday;public String sex;public String getSex() {return sex;}public void setSex(String sex) {this.sex = sex;}public Date getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public Student(){System.out.println("无参构造函数");}public Student(String name){System.out.println(name);}public Student(String name,int age){System.out.println(name+"....."+age);}private Student(int age){System.out.println("私有构造函数");}public void run(){System.out.println("run.....");}public void run(String name){System.out.println("run....."+name);}public void run(String name, int age){System.out.println("run....."+name+"....."+age);}public int sum(int i, int j){return i+j;}private void privateMethod(){System.out.println("privateMethod.....");}public static void staticMethod(){System.out.println("staticMethod.....");}}
package net.csdn.high;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import org.junit.Test;public class RefFieDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RefFieDemo r = new RefFieDemo();r.test1();System.out.println("---------");r.test2();}@Testpublic void test1() throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException{Student s = new Student();Class clazz = Class.forName("net.csdn.high.Student");Field f = clazz.getField("sex");String sex = (String) f.get(s);System.out.println(sex);//类型Class type = f.getType();System.out.println(type);//设置值f.set(s, "nv");System.out.println(s.sex);}@Testpublic void test2() throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException{Student s = new Student();Class clazz = Class.forName("net.csdn.high.Student");Field f = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");f.setAccessible(true);String name = (String) f.get(s);System.out.println(name);//类型Class type = f.getType();System.out.println(type);//设置值f.set(s, "lisi");System.out.println(s.getName());}}