Spring数据库访问之ORM(一)
Spring数据库访问中另外一大模块就是ORM,ORM即对象/关系映射。Spring支持大多数ORM框架,比如Hibernate,JPA,JDO,TopLink和iBatis(Spring2支持iBatis2,现MyBatis3的Spring支持由MyBatis社区开发,并非Spring)。
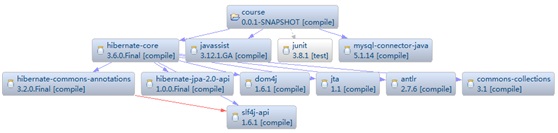
首先我们从单独使用ORM框架开始,来介绍Spring对ORM的支持,以Hibernate为例。使用ORM框架,需要提供持久化类,以课程管理为背景,如下设计课程类:
package org.ourpioneer.course.bean;import java.sql.Date;/** * 课程信息描述bean * * @author Nanlei * */public class Course {private Long id;private String title;private java.util.Date startDate;private java.util.Date endDate;private int fee;//必须提供无参默认构造方法public Course() {super();}//省略其它构造方法,getter和setter等方法}package org.ourpioneer.course.dao;import java.util.List;import org.ourpioneer.course.bean.Course;public interface CourseDAO {public void save(Course course);public void delete(Course course);public void update(Course course);public Course findById(Long courseId);public List<Course> findAll();}package org.ourpioneer.course.dao;import java.util.List;import org.hibernate.Query;import org.hibernate.Session;import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;import org.hibernate.Transaction;import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;import org.ourpioneer.course.bean.Course;public class CourseDAOImpl implements CourseDAO {private SessionFactory sessionFactory;public CourseDAOImpl() {Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();}public List<Course> findAll() {Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();try {Query query = session.createQuery("from Course");return query.list();} finally {session.close();}}public Course findById(Long courseId) {Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();try {return (Course) session.get(Course.class, courseId);} finally {session.close();}}public void save(Course course) {Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();try {tx.begin();session.saveOrUpdate(course);tx.commit();} catch (RuntimeException e) {tx.rollback();throw e;} finally {session.close();}}}<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"><hibernate-configuration><session-factory><property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property><property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///test</property><property name="connection.username">root</property><property name="connection.password">123</property><property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property><property name="show_sql">true</property><property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property><mapping resource="org/ourpioneer/course/hbm/course.hbm.xml" /></session-factory></hibernate-configuration>
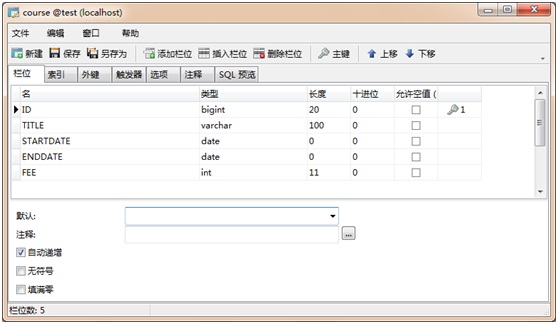
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN""http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"><hibernate-mapping package="org.ourpioneer.course.bean"><class name="Course" table="course"><id name="id" type="java.lang.Long" column="ID"><generator /></id><property name="title" type="java.lang.String" column="TITLE"length="100" not-null="true" /><property name="startDate" type="java.sql.Date" column="STARTDATE"not-null="true" /><property name="endDate" type="java.sql.Date" column="ENDDATE"not-null="true" /><property name="fee" type="java.lang.Integer" column="FEE"not-null="true" /></class></hibernate-mapping>
<repositories><repository><releases><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></releases><snapshots><updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy></snapshots><id>Jboss</id><name>Jboss Repository</name><url>https://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public</url></repository></repositories>
package org.ourpioneer.course;import java.util.GregorianCalendar;import java.util.List;import org.ourpioneer.course.bean.Course;import org.ourpioneer.course.dao.CourseDAO;import org.ourpioneer.course.dao.CourseDAOImpl;public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {CourseDAO courseDAO = new CourseDAOImpl();Course course = new Course();course.setTitle("Spring ORM");course.setStartDate(new GregorianCalendar(2011, 1, 1).getTime());course.setEndDate(new GregorianCalendar(2011, 2, 1).getTime());course.setFee(100);courseDAO.save(course);List<Course> courses = courseDAO.findAll();Long courseId = courses.get(0).getId();course = courseDAO.findById(courseId);System.out.println(course);courseDAO.delete(course);}}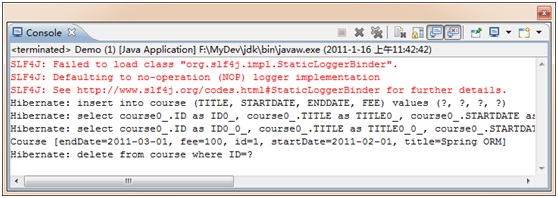
package org.ourpioneer.course.bean;import java.sql.Date;import javax.persistence.Column;import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.GenerationType;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;/** * 课程信息描述bean * * @author Nanlei * */@Entity@Table(name = "course")public class Course {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)@Column(name = "ID")private Long id;@Column(name = "TITLE", length = 100, nullable = false)private String title;@Column(name = "STARTDATE",nullable=false)private java.util.Date startDate;@Column(name = "ENDDATE",nullable=false)private java.util.Date endDate;@Column(name = "FEE",nullable=false)private int fee;// 其余内容不变,省略}<!-- <mapping resource="org/ourpioneer/course/hbm/course.hbm.xml" /> --><mapping name="code">public CourseDAOImpl() {// Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();Configuration cfg = new AnnotationConfiguration().configure();sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();}<dependency><groupId>org.hibernate</groupId><artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId><version>3.6.0.Final</version><type>jar</type><scope>compile</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>jboss</groupId><artifactId>jboss-archive-browsing</artifactId><version>5.0.0alpha-200607201-119</version><type>jar</type><scope>compile</scope></dependency>
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistencehttp://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd"version="1.0"><persistence-unit name="course"><properties><property name="hibernate.ejb.cfgfile" value="/hibernate.cfg.xml" /></properties></persistence-unit></persistence>
package org.ourpioneer.course.dao;import java.util.List;import javax.persistence.EntityManager;import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;import javax.persistence.EntityTransaction;import javax.persistence.Persistence;import javax.persistence.Query;import org.ourpioneer.course.bean.Course;public class CourseDAOImplJPA implements CourseDAO {private EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory;public CourseDAOImplJPA() {entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("course");}public void delete(Course course) {EntityManager manager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();EntityTransaction tx = manager.getTransaction();try {tx.begin();manager.remove(manager.merge(course));tx.commit();} catch (RuntimeException e) {tx.rollback();throw e;} finally {manager.close();}}public List<Course> findAll() {EntityManager manager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();try {Query query = manager.createQuery("select course from Course course");return query.getResultList();} finally {manager.close();}}public Course findById(Long courseId) {EntityManager manager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();try {return manager.find(Course.class, courseId);} finally {manager.close();}}public void save(Course course) {EntityManager manager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();EntityTransaction tx = manager.getTransaction();try {tx.begin();manager.persist(course);tx.commit();} catch (RuntimeException e) {tx.rollback();throw e;} finally {manager.close();}}public void update(Course course) {EntityManager manager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();EntityTransaction tx = manager.getTransaction();try {tx.begin();manager.merge(course);tx.commit();} catch (RuntimeException e) {tx.rollback();throw e;} finally {manager.close();}}}

